Development Report
Related Files:
Development Report 2016
In the past few years, Slovenia has taken a number of positive steps and slightly narrowed its development gap with the EU. Regardless of positive shifts, challenges remain in terms of ensuring a more sustainable improvement to Slovenia’s growth potential and the welfare of its population, which will require more radical structural changes.
Related Files:
Regardless of these positive shifts, challenges remain in terms of ensuring a more sustainable improvement to Slovenia’s growth potential and the welfare of its population, which will require more radical structural changes. To strengthen its growth potential and improve the quality of life and welfare of its population, it is vital that Slovenia increases its productivity and adjusts its social protection systems to demographic changes, i.e. the rising share of the elderly population. Both would also have a positive impact on fiscal consolidation, which is essential for Slovenia to create a stable macroeconomic framework as a basis for sustainable development. However, economic development must also pursue the goal of reducing the environmental burden, and the measures taken towards more efficient use of energy and commodities should be considered an opportunity to increase productivity and competitiveness.
Priority measures should be focused on:
- Establishing strategic development priorities and improving the efficiency of the government and its institutions responsible for making and executing coordinated development decisions;
- Increasing productivity by boosting the innovative capacity of businesses, providing a business environment that fosters entrepreneurship, developing human capital supportive to the competitiveness of the economy and encouraging the more efficient use of digital technologies;
- Ensuring sources of finance for businesses by establishing an effective banking system, faster restructuring of enterprises, improving access to funding for small and medium-sized enterprises and developing the non-bank segments of the financial system;
- Improving the governance of state-owned enterprises and restructuring their ownership;
- Continuing fiscal consolidation through more permanent measures for reducing the structural deficit, particularly in order to ensure the fiscal sustainability of the pension system;
- Adjusting social protection systems to the ageing population, establishing a comprehensive system of long-term care, improving the efficiency of the health system and strengthening its preventive activities;
- Improving the system of labour market flexicurity in order to improve the efficiency of labour force allocation and reduce labour market segmentation;
- Reducing environmental pressures through the more efficient use of energy and raw materials and a transition to sustainable mobility.
Slovenia's development - Indicators:
- Macroeconomic framework
- Factors of competitiveness
- Demographic changes and the welfare state
- Environmental, regional and spatial development
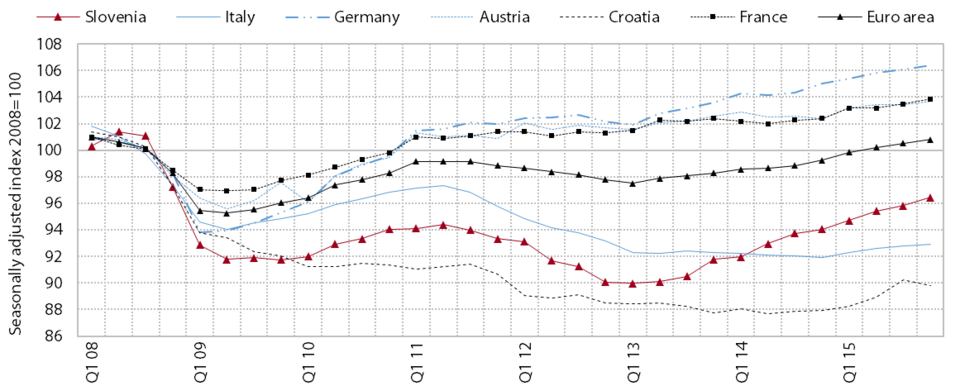
GDP growth continued in 2015 (2.9%), again largely as a result of exports, amid stronger growth in private consumption. Export growth was boosted by rising foreign demand and further competitive gains. Exports remained the main driver of economic recovery, and domestic consumption also continued to rebound. Stronger employment growth and higher average gross earnings translated into further growth in household disposable income and, in turn, a further recovery in private consumption. This was also boosted by consumer confidence, which climbed to one of the highest levels on record. Meanwhile, investment growth slowed owing to a renewed decline in construction investment. This had otherwise increased significantly in 2014, particularly owing to investment in public infrastructure related to the accelerated absorption of EU funds before the expiry of the previous financial perspective. On the other hand, private investment in machinery and equipment was up last year, a trend that had already been suggested by higher profits in the private sector, an improvement in indebtedness indicators and better access to funding. The fall in government consumption gradually came to a halt in 2014 and 2015. Economic growth in the EU strengthened further last year (1.9%), largely on the back of rising private consumption. Despite its higher GDP growth than the EU average in 2014 and 2015, Slovenia remains among the group of countries with the steepest declines in economic activity during the crisis. While GDP for the EU was already slightly above the 2008 level in 2015, Slovenia’s GDP was 4.2% lower than before the crisis.
GDP in Slovenia and its main trading partners
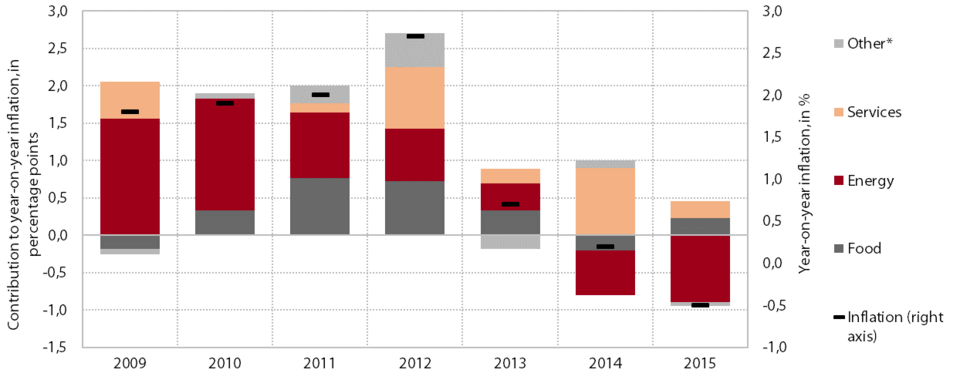
After modest growth in 2013 and 2014, consumer prices were down year-on-year at the end of 2015 (−0.5%) for the first time thus far. As was the case in 2014, price movements last year were significantly affected by commodity price developments on the global markets, especially the continued fall in oil prices. This was mainly reflected in a further decline in energy prices (a contribution of −0.9 percentage points), which was even more pronounced than in 2014. Amid modest domestic consumption, the year-on-year deflation was also partly due to the falling prices of durable goods, but this decline was less pronounced than in previous years. By contrast, the prices of semi-durables were up again last year after modest growth in 2014. Higher prices were also recorded for food (unprocessed) and services. However, at the end of the year, the contribution of services prices was significantly lower owing to the waning effect of a one-off factor. The impact of tax policy measures was also lower than in 2014. We estimate that they contributed around 0.2 percentage points to deflation last year (in 2014: 0.5 percentage points). The price movements in the euro area were also characterised by external factors, but modest inflation was recorded last year (0.2%) after a period of deflation in 2014, amid the strengthening of private consumption, primarily on account of price increases in services and non-energy goods.
Contributions to year-on-year growth in consumer prices inSlovenia
3. Current account of the balance of payments
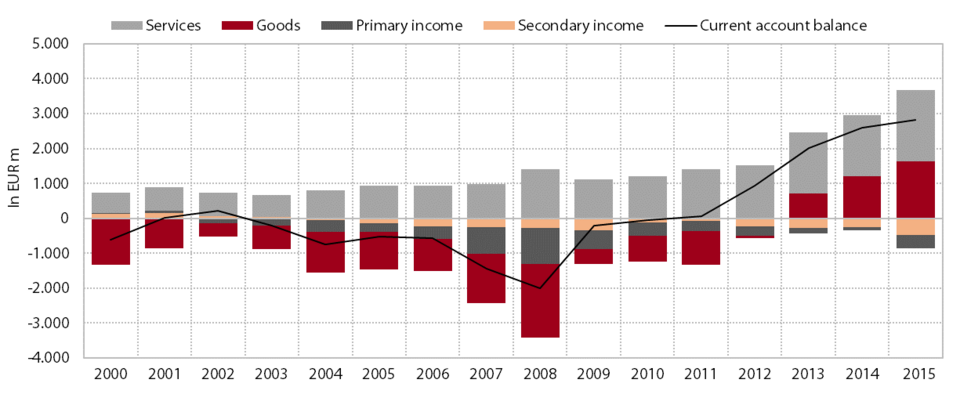
The current account, which recorded a significant deficit at the beginning of the crisis, has been in surplus since 2011; in 2015 the surplus widened further. In the 2011–2014 period as a whole, the surplus increased by EUR 2.5 billion; last year its growth eased and it totalled EUR 2,828 million (7.3% of GDP). In 2015 the surplus in goods trade rose further, by EUR 418 million to EUR 1,628 million. In addition to quantity factors amid faster real growth in exports than imports, the increase was again due to better terms of trade owing to the falling euro import prices for energy and raw materials. The surplus in services trade widened by EUR 318 million last year, to EUR 2,054 million, which was mainly attributable to the larger trade surplus in travel and transport services. Despite the strong growth in domestic household spending on travel abroad, the trade surplus in travel services increased owing to stronger non-resident spending in Slovenia. The larger trade surplus in transport services was chiefly the result of a larger surplus in road transport. The deficit in primary income widened primarily as a consequence of a larger net outflow of direct investment income and totalled EUR 370 million, which is EUR 283 million more than in 2014. Subsidies from the EU budget were also lower. Net interest payments on external debt remained at a similar level: the net interest payments of the general government sector rose further, while the private sector recorded net interest receipts due to the deleveraging of commercial banks and higher domestic investment in foreign debt securities. Income from the work of daily migrants abroad continued to rise faster than income from non-residents working in Slovenia. The deficit in secondary income was higher than in the previous year, mainly on account of a larger net outflow of various current transfers.
Components of the current account of the balance of payments
4. Gross external debt
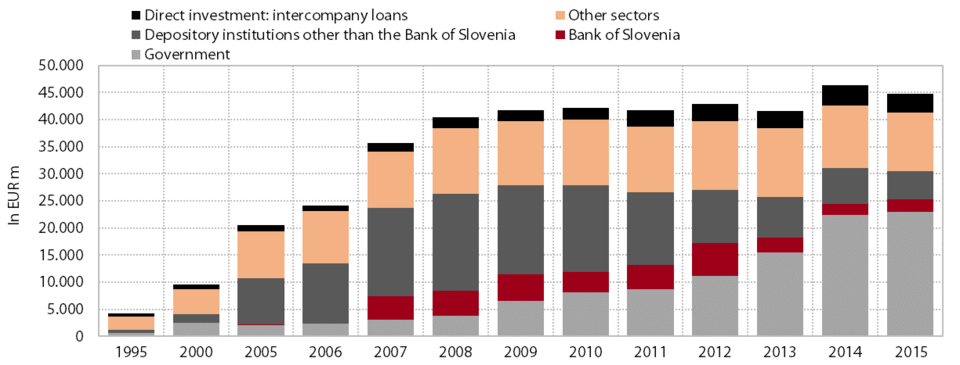
Slovenia’s gross external debt declined in 2015 owing to a further reduction in the debts held by commercial banks and slower growth in general government debt. At the end 2015 gross external debt stood at EUR 44.8 billion, which was down EUR 1.5 billion on the figure for December 2014. It declined as a result of a reduction in long-term debt, which accounted for four-fifths of total debt. In 2015 the commercial banks continued to repay their liabilities abroad, the volume of their debt thus totalling EUR 5.2 billion, which is EUR 12.7 billion less than in 2008. Commercial banks also repaid a portion of their liabilities to foreign portfolio investors, while non-residents started withdrawing their deposits from Slovenian banks. The central bank’s debt expanded slightly last year, by EUR 0.1 billion to EUR 2.2 billion, mainly owing to the recording of euro banknotes in accordance with the EMU system. Other sectors (mostly non-financial corporations) also continued to reduce their debts last year; enterprises mainly made repayments of their long-term loans abroad. After the extensive borrowing since the beginning of the crisis, the general government sector increased its debt by only EUR 0.6 billion last year, to EUR 23.0 billion. The government repaid a portion of its liabilities to foreign portfolio investors, but increased borrowing in the form of loans in order to hedge against exchange rate risk. Debt growth was also underpinned by intercompany loans under direct investment, most of which comprised the loans of Slovenian affiliates to their parent companies abroad. In the structure of debt with regard to guaranties, public debt has expanded since the beginning of the crisis, whereas non-guaranteed private debt has contracted. In 2015 public debt rose again, by EUR 0.6 billion to EUR 23.0 billion. Publicly guaranteed debt contracted by EUR 0.3 billion (to EUR 6.7 billion), owing to a decline in the stock of guarantees to domestic financial institutions. At the end of 2015 public debt accounted for 51.4% of total gross external debt, an increase of 42.1 percentage points over 2008, while publicly guaranteed debt represented 14.9%, down 1.2 percentage points from 2008. Non-guaranteed private sector debt declined by EUR 15.1 billion relative to 2008, totalling EUR 15.1 billion at the end of 2015.
Structure of Slovenia’s gross external debt by sector
5. Net financial position
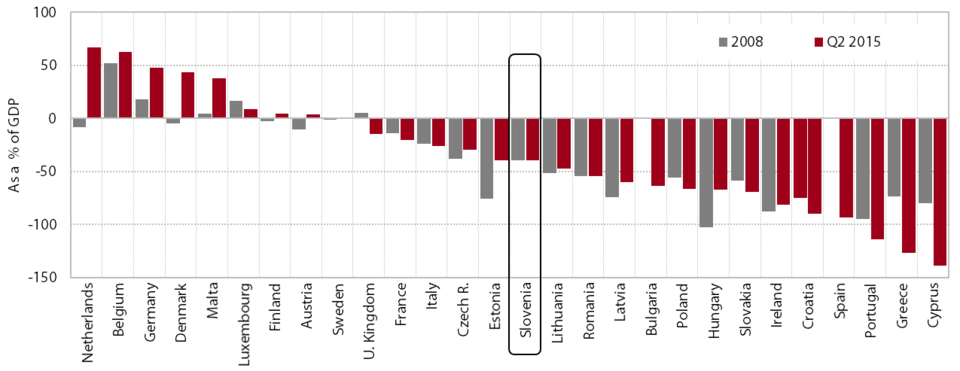
Despite private sector deleveraging, Slovenia’s net financial position has deteriorated significantly since the onset of the crisis owing to increased borrowing by the general government; in 2015 it fell below the 2008 level for the first time in this period. In the early years of the crisis (up to 2012) it had deteriorated mainly due to the accelerated borrowing of the government. It improved for the first time in 2013 as a result of private sector deleveraging, which had otherwise been in progress since 2009. Despite a significant increase in general government gross external debt, in 2014 Slovenia’s net financial position improved further owing to the ongoing private sector deleveraging and a decline in liabilities to the Eurosystem, before falling in 2015 to the lowest level since the beginning of the crisis. Slovenia’s net international investment position was negative, at minus EUR 14.8 billion, or 38.5% of GDP (in 2014: 43.6% of GDP). The improvement reflected an increase in financial assets held abroad (by EUR 0.9 billion) and a decline in external liabilities (by EUR 0.5 billion). The debt-to-GDP ratio was also favourably impacted by the higher nominal GDP. The increase in total claims was mainly due to investment by the BoS, investment funds (except money market funds), insurance companies and pension funds in foreign securities, which is related to the higher yields on foreign financial markets. Short-term trade credits used by enterprises to finance operations with non-residents strengthened, reflecting further growth in exports of goods and services. The government was withdrawing funds deposited at the BoS, transferring them abroad. The stock of outward FDI was somewhat lower, mainly owing to the outflow of equity capital, while the stock of loans granted by Slovenian direct investors was up. The decline in total external liabilities was mainly impacted by further commercial bank deleveraging and the outflow of non-resident deposits from Slovenian banks. Liabilities of Slovenian affiliates to parent companies abroad also declined slightly, as did liabilities from foreign investment in securities, due to the government and commercial banks having repaid a portion of their liabilities to foreign portfolio investors. The amount of inward FDI increased, primarily on account of the inflow of equity capital, which was due for the most part to the debt-to-equity swap. Since 2008 Slovenia has exceeded the indicative threshold of the EU indicator of external imbalance (35% of GDP), but came very close to falling below this figure with the improvement to its net financial position in 2015, and is significantly below the level of the most indebted countries in the euro area.
Net financial position in EU Member States, as a % of GDP
6. General government balance
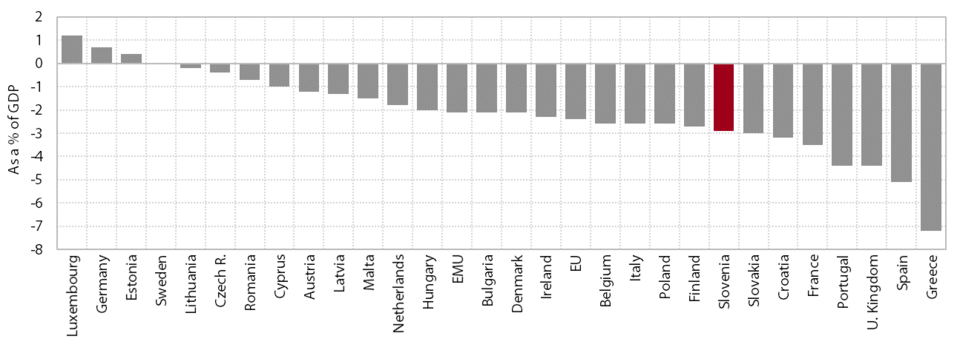
The decline in the deficit to 2.9% of GDP in 2015 was attributable to a further strengthening of economic activity, measures to increase revenue and contain expenditure, and the diminishing effect of one-off factors. Similar to 2014, revenue increased more than expenditure in 2015 (excluding one-off factors). In 2014 and 2015, revenue growth – which until 2014 had been almost entirely due to rises in various non-tax revenues – also stemmed from tax revenues and social contributions, which was attributable to increases in some tax rates, the broadening of the base for social contributions and the recovery in economic activity. On expenditure side, fiscal consolidation was supported by similar measures to previous years, which limited growth in compensation of employees and social benefits and transfers. These were temporary measures, most of which were extended into 2015, so that after declining in previous years, these expenditure categories already recorded growth in 2015. Last year total expenditure growth also stemmed from higher expenditure not only on investment and intermediate consumption, but also current transfers, which expanded partly as a result of one-off factors. As was the case in 2014, the increase in investment expenditure was boosted by funds from the EU budget under the 2007–2013 financial perspective, the absorption of which expired last year. After its decline in 2012 and 2013, the stronger growth of intermediate consumption largely arose from the increase in this expenditure in public institutes in the health care sector; this was made possible by increased HIIS revenue, which had been boosted by the growth in contribution bases; at the end of the year intermediate consumption growth was also underpinned by expenditure related to the management of refugee and migrant flows. Subsidies again numbered among the expenditures that dropped in 2015. They are thus notably lower than in the pre-crisis period, but their role in supporting the corporate sector is being replaced by other instruments (see Chapter 1.2). Interest payments declined for the first time since the onset of the crisis, which was attributable to the more favourable conditions for new borrowing. The largest decline was recorded for expenditure on capital transfers, but in 2014 these had been affected by a number of one-off factors. In 2015 there were significantly fewer one-off factors and their total impact on the deficit (both revenue and expenditure) was negligible (EUR 20 million or 0% of GDP) compared with 2014 (slightly more than EUR 400 million or 1.2% of GDP).
General government balance in EU Member States, 2015
7. General government debt
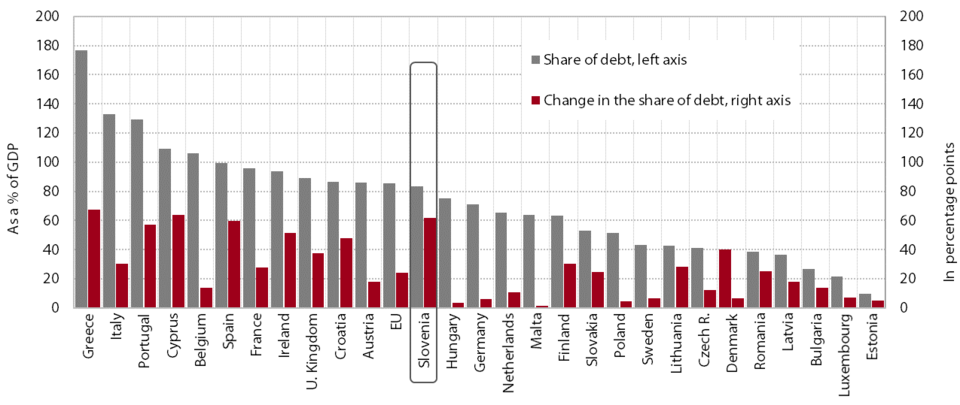
In 2015 general government debt increased further, once again primarily due to the government borrowing for pre-financing borrowing needs in the years to come; however, its maturity is being extended. General government debt expanded by EUR 1.9 billion in 2015 (2.3 percentage points of GDP). This is significantly less than in the previous two years, when a large portion of new borrowing was used for the recapitalisation of the banks, but considerably more than before the crisis when it had been rising by an average of EUR 0.6 billion per year. At the end of 2015, general government debt reached 83.0% of GDP, which ranks Slovenia in the middle among EU Member States, but its growth dynamics have exceeded the EU average ever since the beginning of the crisis. Almost half of the debt increase in 2015 (EUR 0.8 billion) was used to cover the current deficit; the remainder, however, owing to the improvement in borrowing terms, was earmarked for pre-financing the borrowing requirements in the future and increasing the deposit as a hedge against the foreign exchange risk of bonds issued in USD. In 2015 the Republic of Slovenia issued long-term bonds in the amount of just over EUR 2.9 billion. For the first time since independence, they included a 30-year bond (in two issues) in the amount of EUR 575 million with the average interest rate of both issues at 3.139%. The high liquidity of the money market in 2015 was also reflected in the extremely low required yields on short-term debt instruments, which fell below 0% in February 2016. The bulk of debt is still accounted for by central government debt (98% of total debt). The growth in local government debt came to a halt in 2015.
Consolidated general government debt in EU Member States in 2015 and the change of debt relative to 2008
8. Yield on 10-year government bonds

With the continued recovery of the Slovenian and euro area economies and further ECB measures, the yields of Slovenian government bonds dropped further in 2015. After a pronounced fall in 2014 (to 2.2%), the yields on 10-year Slovenian government bonds continued to decline in 2015, most notably in the first quarter. The decline in the yields on Slovenian bonds (as well as the bonds of most euro area countries) in this period was attributable not only to the improvement in the economic situation and a general decline in uncertainty in the EU, but also, for the most part, to the ECB’s announcement of new measures to enhance the functioning of the transmission mechanism. In March 2015 the yield to maturity of the 10-year Slovenian euro bond thus reached its lowest level since Slovenia's admission to the euro area (0.8%). Later in the year the yields rose, not only for Slovenia but also for most of the other countries in the euro area, mainly owing to the uncertainty related to the agreement between Greece and its biggest creditors. After the agreement was signed in July 2015, the required yields of most euro area countries resumed their decline. At the end of 2015 the average yield of the Slovenian euro bonds was thus lower than in 2014 (1.6%). In the first months of 2016, it continued to decline, reaching 1.3% at the end of March.
In 2015 the rating agency Moody’s returned Slovenia's credit rating to investment grade and thus restored its ranking among the countries with low risk. The rating agencies S&P and Fitch preserved their low risk ratings for Slovenia in 2015. Despite the improvement in 2014 and 2015, these ratings remain lower than before the crisis. On the other hand, S&P and Fitch improved their outlooks for Slovenia from stable to positive in 2015, mainly owing to the improvement in domestic economic activity and a decline in political risks regarding the implementation of economic and fiscal policy measures.
Yields on 10-year government bonds denominated in euro, in %
9. Taxes and social security contributions
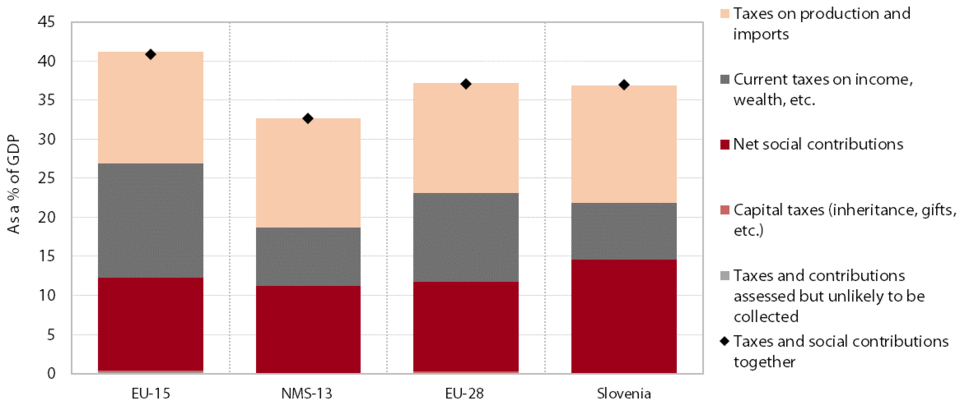
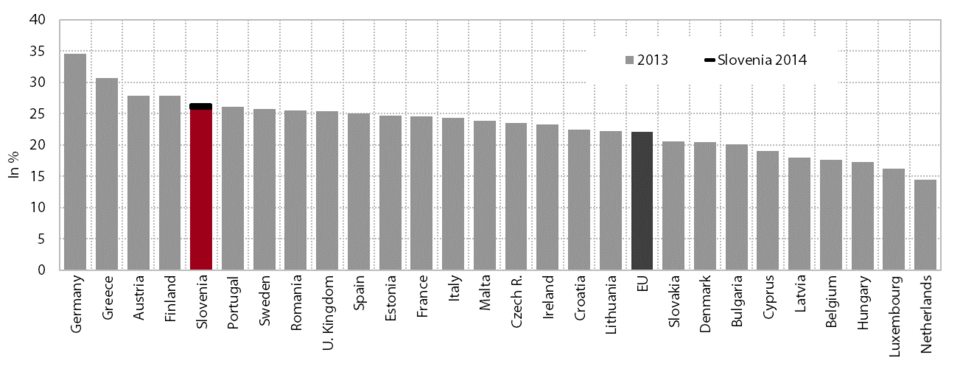
Having increased in relation to GDP since the beginning of the economic crisis, the burden of taxes and social contributions declined slightly in 2014 and 2015 and was similar to the pre-crisis year; in nominal terms, it was still lower than before the crisis. The share of revenue from taxes and social contributions in GDP in 2014 (37.0%) was similar to that in 2008, but below its 2005 peak (−1.3 percentage points). Revenues from taxes were lower than in 2008, while revenues from social contributions were slightly higher, both nominally and as a share of GDP. The nominal decline in tax revenues arises from: (i) a decline in corporate income tax revenue as a result of deteriorated business performance, gradual reductions in the tax rate and increased tax reliefs; and (ii) a decline in personal income tax revenue, mainly as a consequence of lower employment, increased tax allowances and a higher upper limit for the second income bracket. Despite the higher VAT rates, revenue from VAT was still slightly lower, while revenue from excise duties was higher owing to the raised excise duty rates. The bulk of the nominal increase in revenue from social contributions was generated in the first years of the crisis (owing to wage growth, despite the decline in employment); after two consecutive years of decline, they increased again in 2014 but at a lower rate than GDP (despite the adoption of measures to broaden the contribution base).
In 2014 the share of taxes and contributions in GDP in Slovenia was comparable to the non-weighted average of the EU Member States, but the relative weight of social contributions, excise duties and VAT was higher than in the EU. The burden of taxes and contributions was 3.9 percentage points lower than the average of the old Member States and 4.3 percentage points higher than the average of those countries that joined the EU in 2004 or thereafter. Slovenia stood out from both averages with its high burden of social contributions and excise duties; the VAT burden in Slovenia was also higher than the average for the old Member States. The tax burden on corporate income and property (real estate) was lower than the averages of the two groups of countries. In terms of the personal income tax burden, Slovenia ranked between the lower and higher averages for the new and old EU Member States respectively.
The burden of taxes and social contributions, Slovenia, as a % of GDP, Slovenia and the EU, 2014
10. Tax burden by economic function
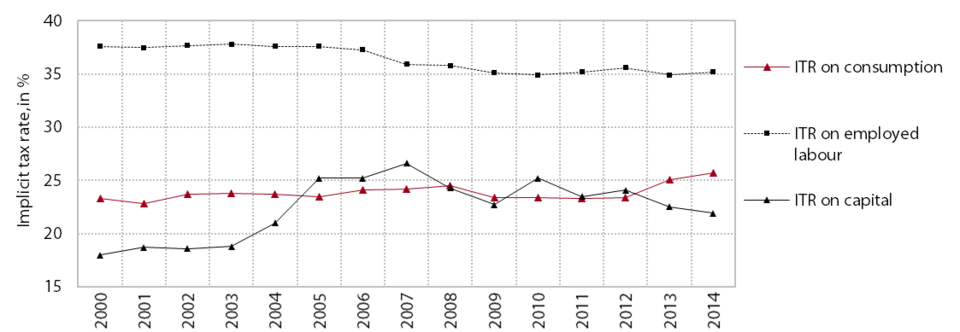
Amid higher rates of excise duty and VAT, the tax burden on consumption is higher than in the years before the crisis, while the effective taxation of labour and capital declined in the period up to 2014. The effective taxation of consumption measured by the implicit tax rate (ITR) on consumption rose significantly after the increase in VAT rates in mid-2013 and reached its highest level in 2014 (25.7%); the increases in excise duty rates also made a significant contribution to the increase relative to the pre-crisis level. The implicit tax rate on labour was relatively stable after a period of decline (2006–2010); in 2014 (35.2%) it was 2.6 percentage points lower than the highest figure in 2003. The effective tax burden on capital continued to decline in 2014. Owing to the gradual reduction in the corporate income tax rate and the increase in tax reliefs in previous years, the implicit tax rate on capital in 2014 (21.9%) was much lower than in 2007, when it reached the highest level after several years of growth. In comparison with the unweighted EU average, Slovenia had higher effective tax rates on consumption and labour and a lower effective tax rate on capital in 2012 according to the latest internationally comparable data available.
Revenues from consumption and labour taxes as a share of GDP exceed the unweighted EU average and have increased more since the beginning of the crisis than the EU average; for revenue from taxes on capital, however, the opposite holds true. In Slovenia taxes on consumption as a share of GDP rose during the period from the beginning of the crisis up to 2012 due to increases in excise duty rates. They rose more than the EU average, which Slovenia had exceeded during the entire period. The share of taxes on labour in GDP was more stable owing to the smaller changes in their tax treatment. After a period of decline (2004–2007), it had been rising gradually and returned close to 20%; this is higher than the EU average, which is related to higher social contributions in relation to GDP. In 2012 the share of taxes on capital in GDP continued to fall even further below the EU average, which recorded a smaller decline during the crisis. The falling of this share in Slovenia is related to (i) the deterioration of companies’ business performance during the crisis; (ii) a decline in the corporate income tax; and (iii) an increase in tax reliefs for fixed capital formation and development.
Implicit tax rates on consumption, labour and capital (as a % of the base), Slovenia (according to ESA 2010)
11. State aid
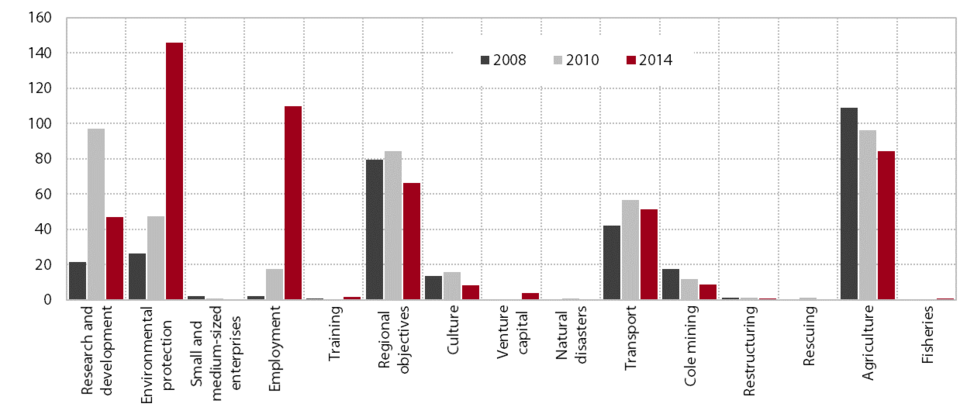
After the strong growth in 2009–2013, the volume of state aid declined in 2014; it was still significantly higher than in the period before the crisis, but the changes to the state aid structure were not entirely appropriate. In 2014 state aid totalled EUR 964 million, of which EUR 433 million was allocated for the stabilisation of the banking sector (under a special scheme termed ‘aid to remedy a serious disturbance in the economy’ or ‘crisis aid’), which is significantly less than in 2013 (EUR 3,317 million). The volume of other aid categories also declined, reaching EUR 531 million (2013: EUR 567 million), but after the increase in 2007–2013 it was still notably higher than before the crisis (Sixteenth Annual Survey on State Aid, 2015). The measures to mitigate the consequences of the crisis (crisis measures) were otherwise removed, and new measures were implemented which focused on environmental protection and employment; in 2014 they accounted for more than a quarter (26.5%) of total aid (except crisis aid), which is a much larger share than in 2010 (15%). In the area of environmental protection, most aid is allocated to payments for renewable energy sources (photovoltaic, hydro-power plants) and the volume of this aid is rapidly rising (in 2014 by 14.3%; the volume of total aid for environmental protection by 24%). Most of the aid for employment (82.6%) was allocated for the promotion of the recruitment of disabled workers; the volume of this aid is also rising rapidly (in 2014 by 12.9%). Meanwhile, the level of aid aimed at enhancing the competitiveness of the economy (for R&D and training, aid for small and medium-sized enterprises) continues to shrink. It fell by a further third in 2014, while the (significantly smaller) volume of aid for regional business investment rose in 2014.
State aid in Slovenia is very high in comparison with the EU. As in several previous years, in 2014 Slovenia was one of the six EU countries with the highest shares of state aid in GDP (excluding crisis aid and aid for railway). With this level of state aid, its reduction would favourably impact the competitiveness of Slovenia's economy and would also be in line with the European Commission’s orientations regarding competition. In the 2008–2013 period, Slovenia also recorded an above-average level of crisis state aid (6th place in the EU in terms of this aid allocated in 2008–2013). Only Ireland, Greece, Cyprus, Spain and Belgium spent more on bank stabilisation in this period.
State aid (excluding crisis aid and aid for railway), as a % of GDP
12. Development of the financial system
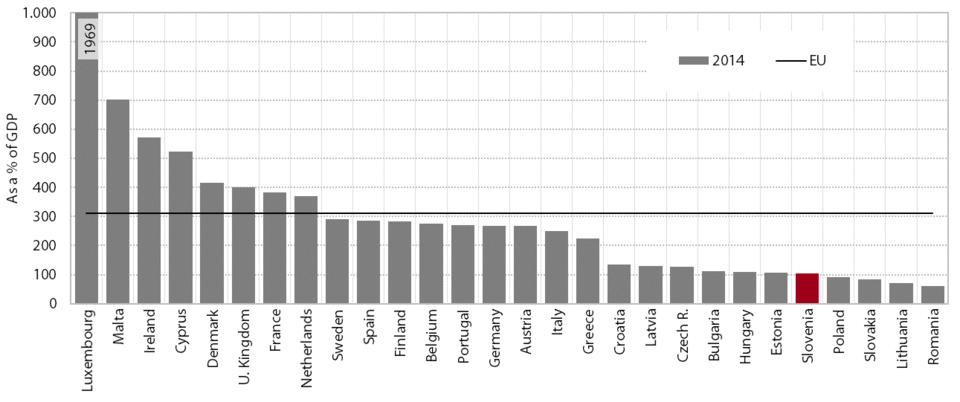
The gap between the level of financial system development in Slovenia and the EU average remains wide; since the onset of the crisis, this widening has been particularly noticeable in the banking sector. The banks’ total assets contracted further in 2015, but the decline was slightly less pronounced than in previous years. The main reason remained the falling volume of loans to non-banking sectors, not only as a result of deleveraging (of enterprises and NFIs in particular), but also modest new lending. With regard to sources of finance, the banks continued to reduce their liabilities abroad, mainly to the monetary sectors and, to a lesser extent, the ECB. In the area of insurance, a sector where the development gap has been the smallest for years, the indicator value declined the least during the crisis. However, Slovenia still lags significantly behind the EU in the share of life-insurance premiums, which, at 1.4% of GDP, reaches less than 30% of the EU average. The low value in this insurance category is also a consequence of the insignificant level of old age savings. This impedes the development of the capital market, which has contracted considerably since the beginning of the financial crisis. After two years of growth, the value of the indicator of market capitalisation of shares as a percentage of GDP rose again in 2015 and totalled approximately 20% of the level in the EU.
Total assets as a % of GDP in EU Member States, 2014
13. Loan-to-deposit ratio
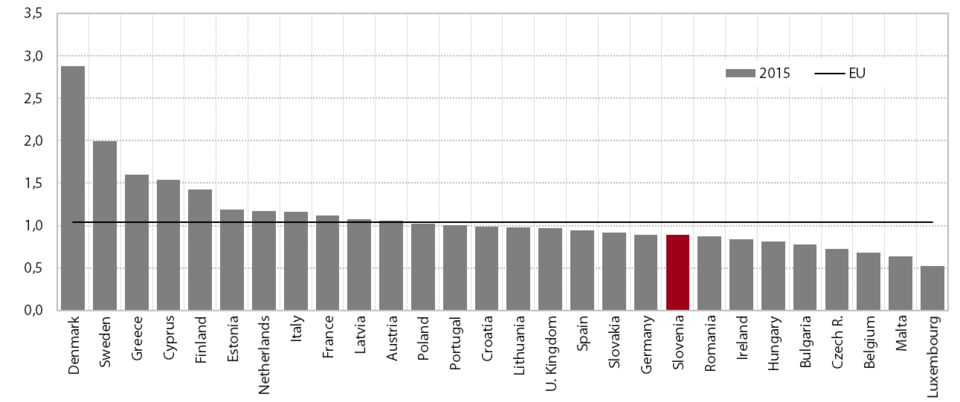
The loan-to-deposit ratio continued to decline in 2015, but at a slightly slower pace. It fell by almost half in comparison to the highest level in 2008. Throughout the period, the decline was primarily due to the contraction of loans rather than growth in deposits. The ratio fell most notably in 2014, owing to the transfer of EUR 1.7 billion in non-performing claims to the BAMC and a concomitant significant increase in non-banking sector deposits due to the higher confidence in the banking system after its stabilisation. In 2014 the amount of deposits thus exceeded the amount of loans for the first time since comparable data have been available. Growth in deposits was more modest throughout the entire period. In 2013 deposits even dropped, mainly owing to the uncertainty regarding the method of banking system stabilisation. The decline in the ratio in 2015 stemmed from both the contraction of loans and growth in deposits. The fall in the total amount of loans was smaller than in 2014. Growth in deposits slowed appreciably, as only overnight deposits were still rising, the main reason for this being the very low deposit interest rates, which no longer compensated savers for the reduced liquidity of their tied deposits.
In the EU the indicator value has also declined since the beginning of the crisis, but from a lower pre-crisis level and to a lesser extent than in Slovenia. During the crisis, the only two countries which recorded a larger decline than Slovenia in their loan-to-deposit ratios were Estonia and Ireland. In some countries, it had already started to rise in 2015. This was mostly due to the growth of loans, with the exception of Greece, where the otherwise strongest growth in the ratio in the EU resulted from an approximately 25% decline in non-banking sector deposits owing to the low confidence of savers in the banking system.
Loan-to-deposit ratios in EU Member States, 2015
14. Non-performing claims

In 2015 the amount and share of non-performing claims in the banking system’s total exposure continued to fall. This decline, having started at the end of 2013 with the commencement of repairs to the banks’ balance sheets, was almost as intense as in 2014, when the largest share of non-performing claims had been transferred to the BAMC; in our estimation, this is also a result of the positive effects of the master restructuring agreements (MRA). At the end of 2015 the volume of non-performing claims amounted to EUR 3.5 billion, which was EUR 1 billion less than in 2014 and EUR 4.3 billion less than before the beginning of the banking system stabilisation in November 2013. It totalled 9.9% of the banking system’s total exposure. Non-performing claims against non-financial corporations continued to contract. Unlike in previous years, a significant contributing factor to the 2015 decline was a reduction in non-performing claims against non-residents, which had not been subject to the transfer of non-performing claims to the BAMC within the process of banking system stabilisation, and fell last year for the first time since 2010. In 2014 and 2015, the speed at which non-performing claims (expressed in relative terms) were reduced also reflected the contraction in bank lending activity (in 2014 the total volume of loans contracted by 12.8%; excluding the transfers to the BAMC, by 7.0% and in 2015 by 6.7%). If the banking system’s total exposure had remained unchanged relative to 2014, the share of non-performing claims would have fallen by 0.6 percentage points more in 2015, and by 1.5 percentage points relative to 2013.
The share of non-performing claims in Slovenia significantly exceeds the EU average, but the stabilisation of the banking system contributed to its relatively faster decline in 2014. The average share of non-performing claims in the EU as a whole has increased since the beginning of the crisis, but much less than in Slovenia. The exceptions are Cyprus, Greece, Ireland, Romania, Croatia, Bulgaria and Hungary, which were particularly affected by the financial crisis. In 2014 the shares of non-performing claims either declined or increased only slightly in most EU Member States. Cyprus stands out with the largest increase (6.3 percentage points), as well as Greece, Italy, Croatia and Portugal (between 1 and 2 percentage points). Slovenia ranked among the countries with large shares of non-performing claims, despite an above-average decline in the indicator value in 2014.
Comparison of the shares of non-performing claims in EU Member States, 2014
15. Indebtedness of the corporate sector
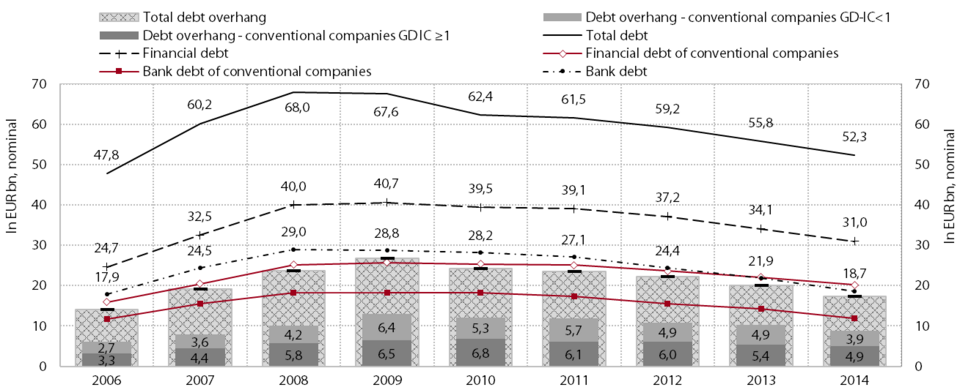
Corporate indebtedness has been declining since 2009, particularly in 2013 and 2014. Financial debt, as the most important part of the total debt of the corporate sector, grew rapidly in the pre-crisis period. This led to significant deterioration in the indicators of indebtedness, which reached their highest levels in 2008 and 2009. In the three years that followed, these indicators improved gradually, particularly during the period from 2012 to 2014. The decline in total debt in this period, especially in 2014, was primarily due the reduction of bank debt (by around 36% relative to 2008; in 2014 alone by around 15%). In the period up to 2011, this debt had been shrinking, primarily as a result of the winding-down of companies, whereas its decline since 2012 has also been due to the intensive deleveraging of surviving companies. In 2014 the indebtedness indicators thus had already come close to the levels of 2006. The debt overhang of Slovenian companies also peaked in 2009, at nearly twice the level of 2006, at which point it fell steadily, most notably in 2014 and 2015. In the entire period under observation, the debt overhang of conventional companies was approximately 50% lower than the overhang of all the companies together. Among over-indebted conventional companies, most are focused on the domestic market, and micro, small and medium-sized enterprises predominate (99.6%). In 2014 they accounted for 60% of the financial debt of over-indebted companies and for 65% of their debt overhang. Debt overhang was highest in the wholesale and retail trade and the repair of motor vehicles (EUR 1.8 billion), manufacturing (EUR 1.7 billion), professional, scientific and technical activities (EUR 1.2 billion) and the energy sector (EUR 1.1 billion). Around 44% of the debt overhang in conventional companies was debt with an interest coverage ratio below 1, which indicates that the company is unable to finance debt with its current operations. As much as 72% of this debt related to the debt of companies that also had negative EBITDA; since the long-term survival of such companies is questionable, the chances of recovering the debt are poor.
The concentration of the financial debt of over-indebted conventional companies is relatively high. In 2014 the ten most indebted conventional companies, which employed 17% of the total workforce of over-indebted conventional companies and generated 22% of their value added, accounted for around 30% of the financial debt of over-indebted conventional companies. Of the most indebted companies, 50 (with a 32% share of the workforce and a 42% share of value added) accounted for almost half of the financial debt of over-indebted conventional companies. Of those, 32 had already been over-indebted before the crisis, while 16 also had a low interest coverage ratio (IC<1) alongside high debts.
Corporate sector indebtedness and debt overhang
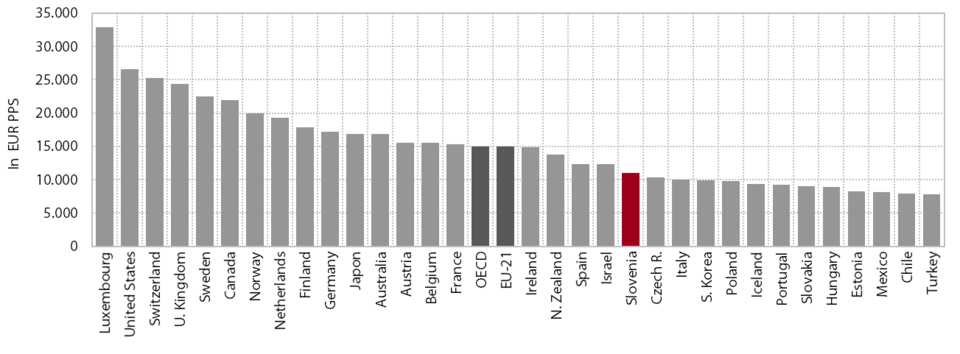
1. Gross domestic product per capita in purchasing power standards
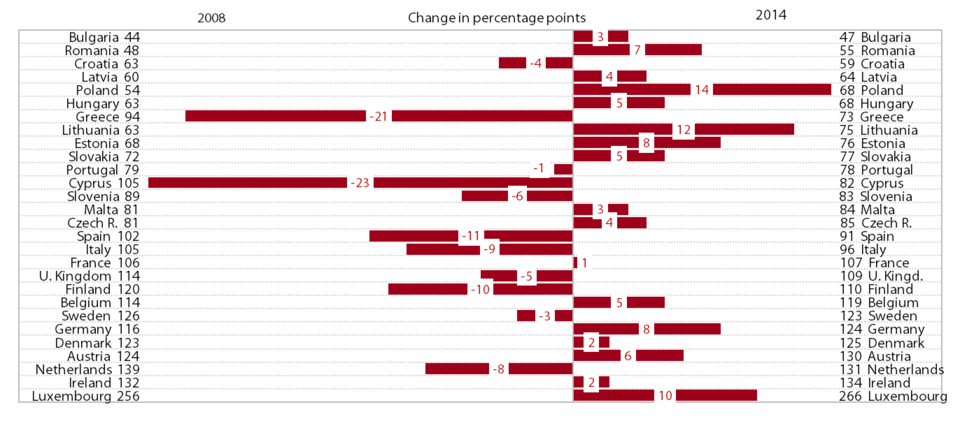
In 2014, for the first time since the onset of the crisis, Slovenia converged slightly to the EU average in terms of GDP per capita in purchasing power standards (PPS), but the gap remained wide (17 percentage points). According to the most recent data, GDP per capita in purchasing power standards totalled 22,600 PPS in 2014. Before the crisis, Slovenia had been catching up with the EU on this indicator, reaching 89% of the EU average in 2008. However, owing to a steeper decline in economic activity, the gap with the EU widened by 8 percentage points over the next five years until faster economic growth in 2014 (Slovenia 3%; EU 1.4%) reduced the gap by 2 percentage points. Current data on economic activity suggest that Slovenia also continued to converge towards more developed countries in 2015.
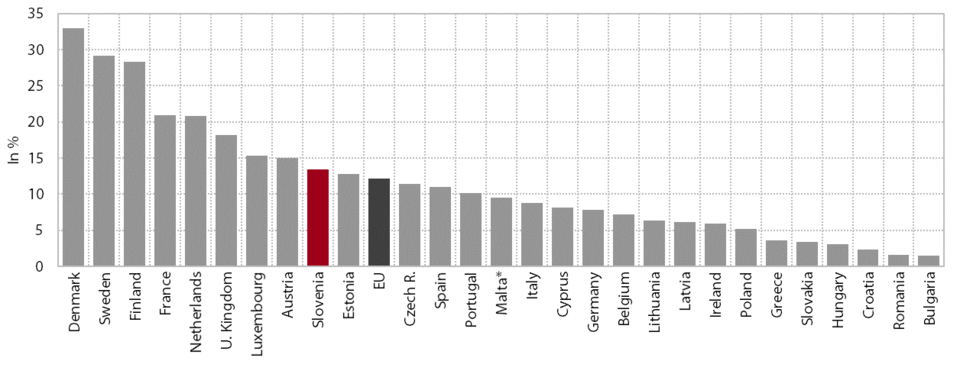
Slovenia remains one of the countries whose relative positions in economic development in the EU have deteriorated the most since the beginning of the crisis. The only countries that have diverged more from the EU average than Slovenia since 2008 are Cyprus, Greece, Spain, Finland, Italy and the Netherlands. In 2008 Greece and the Czech Republic were closest to Slovenia in terms of GDP per capita in PPS (in 2014 these countries were Cyprus, Malta and the Czech Republic). Two of the new Member States, Malta and the Czech Republic, outpaced Slovenia during this period, while some of the new Member States substantially narrowed their gaps with Slovenia, particularly Lithuania and Estonia. In 2014 a total of 15 countries narrowed their development gaps with the EU in comparison with the previous year, of which Slovenia made the most progress (by 2 percentage points); two countries held their positions, but eleven countries fell away, Finland the most (by 3 percentage points). The gap in GDP per capita in PPS between the EU Member States – at 1:9.8 (Romania/Luxembourg) at the beginning of the previous decade – has been narrowing over the years, falling to only 1:5.7 in 2014 (Bulgaria/Luxembourg).
GDP per capita in PPS, change in 2008–2014 (EU=100)
2. Labour productivity
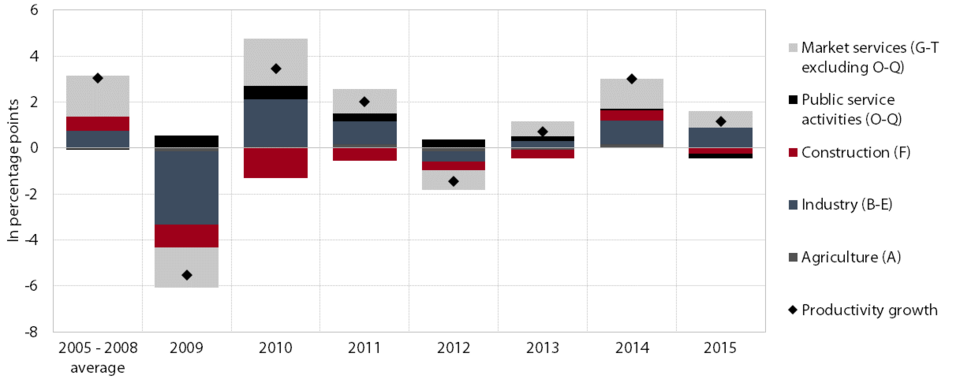
Only during stronger economic activity in 2014 and 2015 did labour productivity exceed pre-crisis levels. A sharp fall in economic activity at the beginning of the crisis caused labour productivity to decline by as much as 6.1% in 2009. Labour productivity growth in subsequent years (except 2012) mainly stemmed from the adjustment of employment to the reduced economic activity and was, in the absence of economic recovery, much more modest than before the crisis and insufficient to expedite convergence to pre-crisis figures. Only in 2014 and 2015 did the increase in GDP become the main driver of growth. However, with the concurrent increase in employment, productivity growth remained significantly below the long-term average seen prior to the crisis (before the crisis, the ten-year average was 3.8%). Modest growth since the beginning of the crisis, amid weak intra-industry productivity growth in most sectors, was also due to the contraction in some parts of the economy that were most affected by the crisis, particularly construction and manufacturing (after 2009 these sectors were characterised by the significant negative contribution of the inter-industry component to productivity growth). Owing to stronger intra-industry growth, manufacturing activities have nevertheless been a major factor in the recovery of productivity since 2009 (see Figure). Alongside manufacturing, market services also made a substantial contribution to productivity growth during this period, particularly knowledge-intensive services and transportation. In 2014 the construction sector had much to do with the improvement, but in 2015 this sector’s contribution reverted to negative.
Productivity of Slovenia’s economy remains low by international standards. Before the crisis, productivity (expressed in purchasing power standards) was at 83% of the EU average, but had already stopped converging to the EU average several years before the crisis. In 2009 and 2010, Slovenia’s productivity gap widened by another 4 percentage points amid less favourable GDP movements, and persisted at a very similar level over the next three years. It narrowed more noticeably only in 2014, but productivity remained low compared with the EU (82% of the EU average).
Sectoral contributions to productivity growth, Slovenia
3. Market share

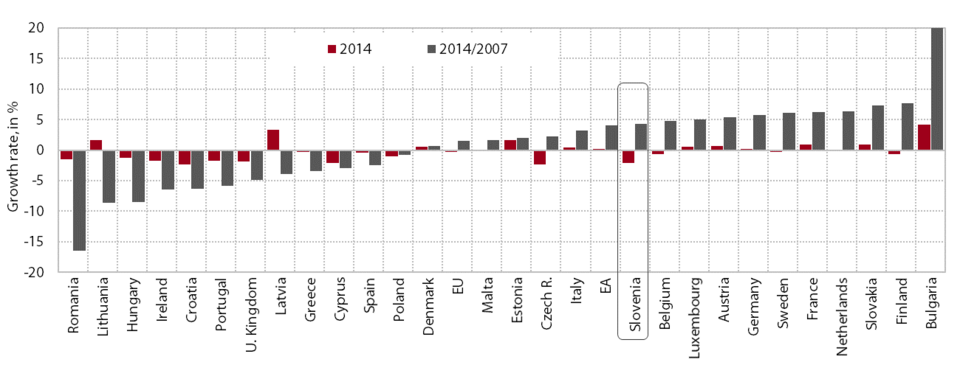
In 2014 the market share of merchandise continued to grow. In the period 2008–2012 Slovenia experienced one of the largest declines in the EU in terms of the share in global merchandise trade (−22%), which was partly a consequence of the regional and product structures of the country’s exports (see Development Report 2013, 2014). The decline on the markets of the 14 key trading partners in this period was approximately half lower; on the EU market, around two thirds lower. In 2013, however, these negative dynamics turned positive, and this trend continued in 2014. During this period Slovenia was one of the EU countries with the highest growth in world market share. Its fall relative to 2007 was, consequently, around a third smaller: on the markets of its main trading partners Slovenia has already achieved pre-crisis levels while it has exceeded these in the EU. The available data for the first nine months of 2015 indicate further growth on the EU market, but at a slower pace. On the world market and the markets of the main trading partners, Slovenia’s market share declined slightly, mainly owing to the effects of the structure of Slovenia’s merchandise exports (see also Chapter 2.1).
The growth of Slovenia’s world market share in 2013 and 2014 was a consequence of a general increase in the shares on its main regional and product markets, which were also some of the most dynamic. More specifically, the growth in import demand on these markets was, for the most part, higher than on the global market. Market share growth was recorded not only in Germany, Italy, Austria, Croatia and France, but also in Hungary, Poland, the United Kingdom, the US and Russia. In terms of factor intensity, the market shares of all product groups expanded in 2013–2014, the most important SITC sections being medicinal and pharmaceutical products, iron and steel, non-ferrous metals, manufactures of metals, machinery specialised for particular industries, road vehicles, miscellaneous manufactured articles, and petroleum and petroleum products.
World merchandise market shares of EU Member States, growth rates in %
4. Unit labour costs
In 2015 unit labour costs declined again. After increasing for three consecutive years under the impact of strong wage growth (2008 and 2010) and a decline in labour productivity (2009), real unit labour costs dropped in 2011 for the first time since the beginning of the crisis owing to the slower growth of wages. When labour productivity fell again in 2012 due to lower economic activity, the growth in real unit labour costs resumed despite a concomitant decline in wages. With renewed labour productivity growth, unit labour costs have been declining without interruption since 2013, first as a result of falling employment and since 2014 under the impact of rising economic activity.
In 2015 the unit labour costs in manufacturing were already lower than before the crisis, but were still higher in the economy as a whole. In 2008–2009, a strong contraction in foreign demand led to an above-average decline in value added and, consequently, labour productivity in manufacturing. Real growth in unit labour costs was therefore higher, despite the more modest growth of wages. In manufacturing, real unit labour costs had already started to decline in 2010 and had fallen much further by 2015 than in the economy as a whole. More specifically, with a rebound in foreign demand, labour productivity growth in the manufacturing sector was higher than in the economy as a whole due to a larger increase in value added and a steeper decline in employment. Growth in compensation per employee was also higher (partly due to the impact of the increase in the minimum wage) but lower than the growth of labour productivity.
The manufacturing sector improved its position relative to the EU in comparison with 2007, but the relative position of the economy was worse than before the crisis. Up to 2010, Slovenia had been among the EU Member States with above-average growth in real unit labour costs in manufacturing; since 2010, however, the country has been experiencing an above-average decline. In 2015 real unit labour costs were 2.6% lower than in 2007 (2.2% higher in the EU). In the economy as a whole, real unit costs were 3.2% higher in this period (0.9%).
Real unit labour costs in Slovenia and EU Member States
5. Structure of merchandise exports by factor intensity
The changes in the structure of merchandise exports towards increasing the share of exports of high-technology goods have been less pronounced recently than at the beginning of the crisis. The share of high-technology products increased to a greater extent particularly in the first years of the crisis (2008 and 2009), when the shares of other, less competitive, industries started to contract. Since 2009, the share of high-technology products has also been constantly strengthening owing to the growth in the absolute values of their exports. This was mainly underpinned by growth in pharmaceutical exports, which had been above average until 2013 before slowing notably in 2014. The share of high-technology products in merchandise exports therefore also fell slightly. Although this figure was one of the highest recorded until that point, it was still below the EU average (by 4.3 percentage points). Relative to the beginning of the crisis, the gap with the EU average has halved and, in recent years, the significance of these products in the structure of our exports has also been above the average for new EU Member States. Medium-technology products otherwise still account for the largest share in the merchandise export structure. Significantly boosted by road vehicle exports, this figure rose slightly in 2014 after four years of decline.
The share of products with low value added in merchandise exports has recently stopped falling. Their significance had been declining for a number of years, primarily owing to the falling share of labour-intensive products; the share of low-technology products has also fallen since the start of the economic crisis. Exports of products with low value added have proved to be very vulnerable to competition from countries with lower labour costs, with the share of textile products, furniture, paper and paperboard exported having contracted, particularly since Slovenia’s accession to the EU. Since 2010 onwards, the decline in these sectors has also been reflected in the deterioration in cost competitiveness due to the substantial statutory increase in the minimum wage. The relative share of products with low value added, which has otherwise been relatively stable in the last two years, has therefore been gradually approaching the EU average (in 2014 it was still 3.5 percentage points higher than the EU average).
The share of resource-intensive products rose notably after 2009, mainly on the back of higher volumes of trade in primary products. The increases in the shares of electricity and petroleum product exports were mainly underpinned by higher volumes of trade in these product groups (re-exports). Owing to lower electricity exports, the share of resource-intensive products otherwise declined slightly in 2014 after several years of growth, but remained significant.
6. Knowledge-intensive market services
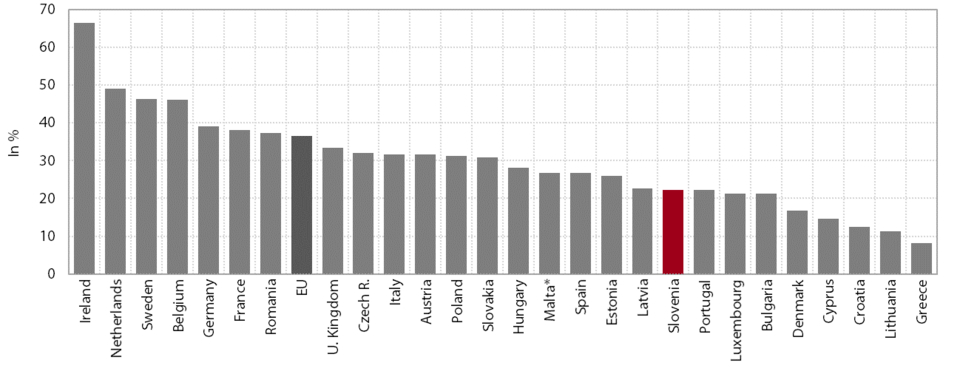
With a further increase in sales revenues on foreign markets, knowledge-intensive market services exceeded their pre-crisis level in 2014. After the beginning of the crisis, it was only in 2013 that the value added of these services started to rise notably, whereas in the EU this figure had already exceeded the 2008 level in 2011, and was 5.5% higher than before the crisis in real terms in 2013 (in Slovenia, 2.8% higher in 2014). The slower recovery among this group of services in Slovenia was mainly due to sectors that are more focused on the domestic market (where demand had contracted substantially in the first years of the crisis) and have only recently started to seek opportunities abroad. In 2014 the value added for these services was 13.5% below the pre-crisis level, whereas in the EU this figure had already exceeded the 2008 level in 2011. On the other hand, the value added of computer programming and legal and accounting services, which have seen increasing sales revenues since 2009, primarily on foreign markets, was 23.7% above the 2008 level in 2014 in Slovenia, as opposed to only about 8% in the EU (data for 2013).
Despite growing sales revenues on foreign markets, the share of knowledge-intensive market services in total exports of services in Slovenia was much smaller than in the EU. Between 2010 and 2014, this share increased by 1.4 percentage points to 22.3%, while the EU average rose by 3.5 percentage points to 36.5%. The smaller share of knowledge-intensive services in the export structure can otherwise be partly attributed to the relatively large share of exports of travel and transport services related to Slovenia’s natural conditions and strategic position; however, the stagnation in the share of knowledge-intensive services on foreign markets also reveals their low export competitiveness (see Section 2.1). This is particularly the case for the following sectors, where the share of exports is smaller than the EU average: computer services (by 7.7 percentage points), technical, trade-related and other administrative and support service activities (4.1 percentage points), professional and management consultancy services (3.5 percentage points) and R&D activities (2.3 percentage points). The share of telecommunications (3.3 percentage points) and information services (0.1 percentage points) recorded in the export of services was larger than in the EU, and this trend was continuing.
Share of knowledge-intensive non-financial market services in total exports of services, 2014
7. Network industries
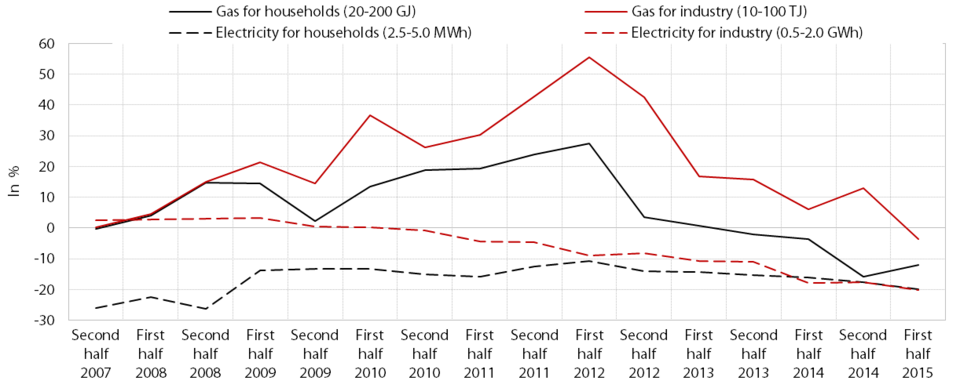
In electronic communications, competition is fairly strong in terms of broadband internet access, but competition in mobile telephony still lags behind the EU average. Fixed telephony (with the exception of the growing share of internet (VoIP) telephony) has been losing market share in recent years, and is increasingly being replaced by mobile telephony. Market concentration in this segment is relatively high, and approaching the EU average only slowly. Broadband internet access is the most competitive market, with the market share of the leading provider already below the EU average. According to the most recent data available, the prices of fixed and mobile telephony services were generally lower in Slovenia than in the EU, but they dropped to a lesser extent in Slovenia than in the rest of the EU for the whole period of 2010–2015.
Regarding the supply of electricity and gas, competition is spurred by numerous provider switches. After the deregulation of the market in 2007, the number of electricity supply switches increased markedly only at the end of the previous decade, peaking in 2012 (over 55,000 or 5.9% of customers), before decreasing slightly by 2014 (32,000 or 3.5% of customers). On the electricity generation market, the competition rate is low (in 2014 the Herfindahl-Hirschman Index (HHI), a concentration index, was 4,569) but comparable with the EU. Competition on the retail market is stronger. In the period from the deregulation of the electricity market up to 2014, the HHI for electricity supply to the consumers on the distribution network dropped from 2,032 to 1,773. The concentration of the suppliers changed to an even greater extent, with the share of the three principal providers falling from 70% in 2007 to just above 50% in 2014. In the first half of 2015, the retail price of electricity for households and industry, excluding taxes, was around 20% below the EU average. On the natural gas market, the arrival of a new provider led to sharp price falls in 2012; in the first half of last year, the gas price (excluding taxes) for households and industrial consumers was 12% and 4% lower than the EU average respectively. After almost no instances recorded of providers being switched in previous years, the switching rate surpassed 11,000 or 8.6% of customers in 2012, before falling to 3.6% by 2014.
Discrepancies in energy prices between Slovenia and the EU average
8. Foreign direct investment
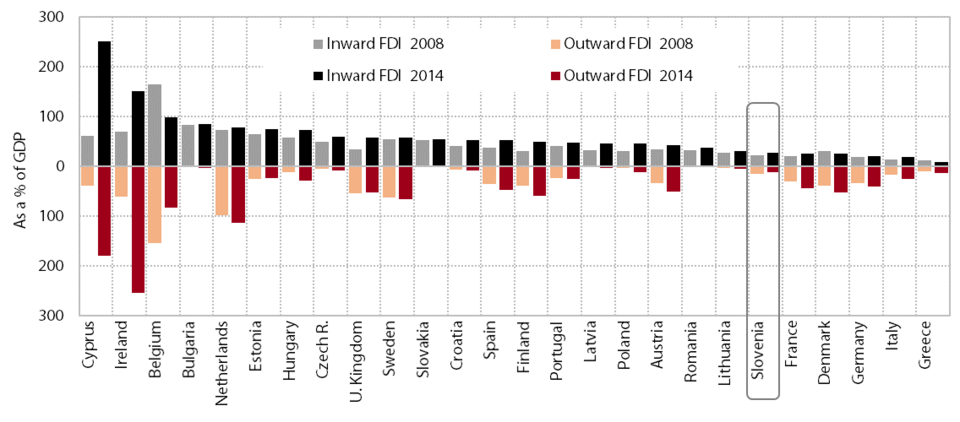
After very low inward FDI until 2013, inflows in 2014 and 2015 indicate a significant increase, while outward FDI remains modest. After a modest improvement in 2010–2013, the stock of inward FDI rose more notably in Slovenia in 2014 for the first time in a long period (by 13.9%). Outward FDI stock, having been decreasing in 2010–2013, rose slightly in 2014 (by 2.6%), but was still 13.5% below its 2009 peak. The equity capital inflows of inward FDI rose notably in 2014 and 2015: in 2014 they amounted to EUR 1,447.0 million and in the first ten months of 2015 to EUR 1,184.8 million, compared with only EUR 1,354.6 million reached in the entire previous five-year period (2008–2012). This is primarily due to the renewal of the privatisation process and the generally higher sales of equity stakes in Slovenian companies. The SPIRIT survey conducted among companies with foreign capital in Slovenia indicates increased sales (58% of companies surveyed) and employment (37%) for a significant portion of these companies, with 32% of companies also planning to expand their activities in 2016. Outward FDI recorded equity capital outflows from Slovenia in 2015 that were at approximately the same level as in 2014, which is significantly lower than in 2013.
Slovenia remains among the EU countries with the lowest inward FDI stock as a share of GDP. Despite a considerable increase in 2014 (to 27.2% of GDP), Slovenia remains among the EU countries with the lowest stock of inward FDI, and the smallest increase in inward FDI stock as a share of GDP over the long term. A smaller share of inward FDI relative to GDP is recorded only by Greece, Italy, Germany, Denmark and France. In terms of outward FDI relative to GDP, Slovenia – among the new Central European EU Member States – lags behind only Hungary and Estonia.
Stocks of inward and outward FDI, as a % of GDP
9. Entrepreneurial activity

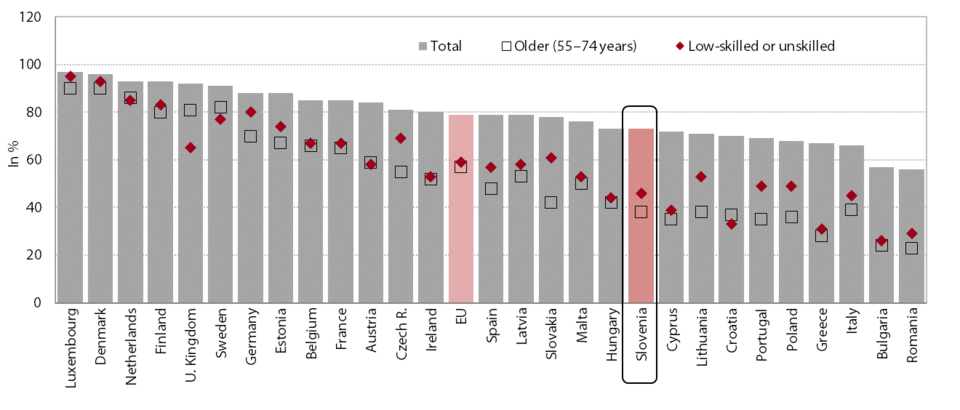
Early-stage entrepreneurial activity dropped for the second year in succession, falling below the level achieved just before the crisis. According to data from the Global Entrepreneurship Monitor (GEM), the rate of total early-stage entrepreneurial activity (TEA-index) declined further in 2015 after peaking in 2013. This was largely due to a decline in the share of nascent entrepreneurs (entrepreneurs running businesses for less than three months), with the share of new entrepreneurs (those who have been in business for less than three and a half years) remaining at the same level for the fourth consecutive year in 2015. Opportunity-driven early-stage entrepreneurial activity has been steadily declining since 2012, thereby diverging from the level reached before the beginning of the crisis. Necessity-driven entrepreneurial activity remains relatively high, but dropped slightly in 2015. In 2015 early-stage entrepreneurial activity also declined in the EU, but is still higher than in 2008 (5.3%). Amid a concomitant contraction in established businesses, total entrepreneurial activity in Slovenia also dropped further in 2015, falling below the pre-crisis level.
Newly established enterprises have accounted for only a modest share of total employment in recent years. Business demography statistics show slower growth in the number of active enterprises in the first years after the beginning of the crisis, but that this accelerated in 2013, the year for which the most recent data are available. The bulk of improvement in 2013 arose from a significant increase in the number of newly established enterprises (without a predecessor), as had already been indicated by GEM data on early-stage entrepreneurial activity, which peaked in 2013. Moreover, the number of deaths of enterprises without a successor declined noticeably in 2013 for the first time since the onset of the crisis. Entrepreneurial dynamics were at their most beneficial in knowledge-intensive services (births 2013: 14.8%; deaths 2013: 6.7%), where the number of newly established enterprises rose by two-fifths, whereas the number of deaths declined by one-tenth. However, the number of employees in newly established enterprises accounted for only a modest share of all employed persons (1.4% in 2013, slightly more in knowledge-intensive services). According to the GEM survey, one of the reasons for this may be the large share of new enterprises established out of necessity, in all likelihood as a result of unemployed people becoming self-employed. The share of high-growth enterprises is therefore among the smallest in the EU, although Slovenia has a relatively high enterprise birth rate and low enterprise death rate by international standards.
Share of high-growth enterprises in the total business economy (NACE activities B–N)*, 2013
10. Share of the population with tertiary education
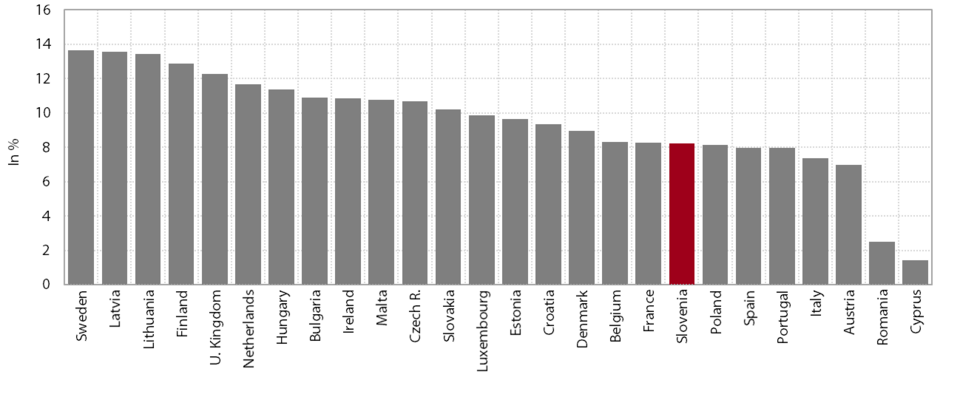
The share of adults with tertiary education is increasing, having kept pace with the EU average since 2014. This trend is a consequence of a long period of high participation of young people in tertiary education, and the structural effect of the transition of younger, more educated generations into higher age groups. The share of women with tertiary education is higher than the corresponding share of men and above the EU average, and the gap between the two groups is widening. With the number of graduates falling since 2013 owing to a decline in student enrolment due to the smaller generations of young people, growth in the share of tertiary educated people is expected to slow in the years to come.
The share of tertiary educated people, which is generally above the EU average, is rising fastest in younger age groups. The only exception is the 25–29 age group, where the share of tertiary educated people lags behind the EU average due to low study efficiency (protracted studies). More favourable developments are recorded for the 30–34 age group, where the share of tertiary educated people stood at 43.6% in 2015 (EU 38.6%), which is higher than the Europe 2020 Strategy target of 40%. Its rapid growth is the result of several years of high participation of young people in tertiary education. Cedefop projects the share of tertiary educated people in this age group to rise to over 50% by 2020 and to 59% by 2025. The share of the tertiary educated people in the 35–44 age group is also higher than the EU average. In terms of meeting the business sector’s requirements, the improvement to the education structure of the population is a positive development; according to Cedefop forecasts for 2015–2025, most job opportunities will be for tertiary educated people and their share in total job opportunities in Slovenia is expected to be higher than the EU average. Nevertheless, the key factor in terms of filling job vacancies that require tertiary education is the structure of graduates by field of study, which is not sufficiently matched to the business sector's needs.
Share of the population aged 30–34 with tertiary education, 2nd quarter, in %
11. Education expenditure
Public and private expenditure on education (as a % of GDP) is similar to the international average. In 2014 public expenditure accounted for 4.99% of GDP and was significantly lower than Slovenia’s long-term average. It has been declining since 2012, largely owing to the effects of fiscal consolidation measures. A decline was recorded in all levels of education except for pre-primary education. Expenditure on tertiary education dropped the most, owing to a decline in transfers to students/households and expenditure on educational institutions. In comparison with the long-year average before 2012, public expenditure was thus lower at all levels except for pre-primary education. By international comparison, Slovenia has higher public expenditure at the primary level (which includes the first six grades of elementary school in Slovenia), with expenditures at upper-secondary and tertiary levels comparable with the EU-21 average (OECD countries). Private expenditure on education stood at 0.67% of GDP in 2014, which is close to the long-term average and, according to data for 2012, higher than the EU-21 average. However, this does not hold true for expenditure on tertiary education, which is the same as in the EU-21 and was below the long-term average in 2014.
After increasing for several years, the expenditure (both public and private) per participant in education declined in 2012 but remained above the long-term average. Relative to the EU-21 average, it remained higher for pre-primary and primary levels of education. Expenditure on upper-secondary and tertiary levels remained significantly lower, which is attributable to the high participation of young people in education. In 2012, expenditure on education per participant declined at all levels of education (particularly upper-secondary), with the exception of tertiary education where expenditure also rose in the longer term. This is related to a decline in enrolment since 2010 owing to smaller generations of young people and the fact that the level of public funds in the higher education funding system is not linked to the number of students enrolled.
Expenditure on educational institutions per participant at the tertiary level of education, in PPS USD, 2012
12. Participation of adults in lifelong learning
The participation rate for adults (aged 25–64) in lifelong learning (formal and non-formal education) in 2015 was 13.3% and above the EU average, although it declined during the crisis. It started to fall after 2010, but in 2015 this decline almost came to a halt. Participation in lifelong learning remains above the EU average, but has diverged substantially from the strategic objectives set due to the decline during the crisis (as a consequence of the unfavourable economic situation, labour market conditions and austerity measures in the public sector). In 2015 it was lower than the objective of the strategic framework for European cooperation in education and training (Education and Training 2020/ET 2020), which is 15%, and even lower than the objective of the Resolution on the Slovenian Master Plan for Adult Education 2013–2020, which is 19%. The participation of less educated people and older people, the two main target groups of the resolution, is particularly modest (the participation rate for older people fell further during the crisis).
The participation of working-age population (25–64) in lifelong learning also declined during the crisis. In 2014 it dropped for the fourth year in succession but remained higher than the EU average (13.4% in Slovenia; 12.2% in the EU), although the gap narrowed significantly during the crisis. In 2008–2014, despite increasing in the EU, participation in lifelong learning declined across all occupational groups and most sectors. It was particularly low for people in occupational groups with lower incomes, who are less able to afford education. In 2014 this figure was also lower than the EU average, but in other occupational groups it was higher. Broken down by sector, participation in lifelong learning in 2014 was highest in financial and insurance activities (where it exceeded that EU average the most) and lowest in the construction sector. Although it declined during the crisis, it remains above the EU average in most sectors. Despite the austerity measures in the public sector, participation in lifelong learning is also high in education, health and social work, and public administration.
Participation of employed persons aged 25–64 in lifelong learning, 2014, in %
13. Gross domestic expenditure on research and development
After a long period of increases, gross domestic expenditure on R&D (GERD) declined in 2014, reaching 2.39% of GDP; this was higher than the EU average, which is stagnating. At −5.0%, the real growth rate of GERD was negative for the second consecutive year. In the 2009–2014 period, R&D investment rose in real terms, by 25.0%, which was significantly more than in the EU as a whole. This was mainly due to the business sector, which increased R&D investment by 47.4% in real terms, and partly due to the higher tax relief. In 2014 the total amount of R&D tax relief claimed stood at EUR 228.6 million; in 2009–2014 it totalled EUR 855.6 million, almost a third of which was claimed by the pharmaceutical industry. In 2012–2014 around 10% of beneficiaries from large companies claimed around two-thirds of the total amount of R&D tax relief, whereas around half of the beneficiaries were micro companies, which claimed only a tenth of all relief. In 2014 the business sector increased R&D investment by 1.8% in real terms and its share of total R&D funding to 68.4%, which is significantly above the EU average (2013: 55.0%). The share of researchers in the business sector is also rising along with R&D investment. In 2014 it rose to 54.1%, having exceeded the EU average (48.8%) since 2010. The R&D expenditure of the public sector (the government and the higher education sector) has been shrinking since 2012, and in 2014 this figure was nominally the same as in 2008. Funds from abroad remain an important source of R&D funding in Slovenia, but they declined for the first time in real terms in the 2009–2014 period upon the completion of projects from the previous financial perspective. In 2013 the majority of foreign funding for Slovenian R&D came from investment by the European Commission and the business sector abroad.
R&D expenditure by sector, Slovenia
14. Science and technology graduates
Despite a decline in the annual number of science and technology graduates, this figure is still higher than at the onset of the crisis; their share is also higher than the EU average. In 2014 the number of science and technology graduates dropped for the second successive year because of demographic factors (the falling number of young people available for enrolment in tertiary education). Although their share of this demographic is no longer growing, at 26.1% it was still significantly higher than in 2008. The movements of the number of science and technology graduates per thousand population aged 20–29 were also more favourable during the crisis. These movements are a consequence of programmes aimed at the popularisation of these fields of study among young people; however in the past few years they have no longer been able to cover the demographic deficit. Given the declining generations available for enrolment in tertiary education, unfavourable trends can also be expected in these fields in the future. This could lead to a gap in the supply of graduates, which in turn could also be exacerbated by tertiary educated young people moving abroad. The developments in sponsorship scholarships are also unfavourable. The potential for improving enrolment in science and technology programmes involves strengthening career counselling for young people and, in particular, encouraging the participation of women, as the share of women enrolled in science and technology programmes in the 2014/15 academic year was only 30%.
The share of doctors of science and technology is also significant in Slovenia. This figure has been above the EU average for the entire period. This has partly been attributable to government incentives (Young Researchers, Young Researchers in the Economy), which are mainly focused on science and technology (the share of expenditure on this field has accounted for over 60% of total expenditure on young researchers since 2006; in 2014, it totalled 64.5%). In 2008–2014 the total number of science and technology graduates rose from 199 to 1,882. In 2014 the number of students enrolled in doctoral studies declined, as was the case in other fields, which can be attributed to cuts in public funds for young researchers, the expiry of the innovative scheme for co-financing doctoral studies and poorer prospects for employment since the beginning of the crisis, particularly after the introduction of austerity measures in the public sector in 2012.
Share of science and technology graduates in the total number of tertiary education graduates, 2013
15. Intellectual property
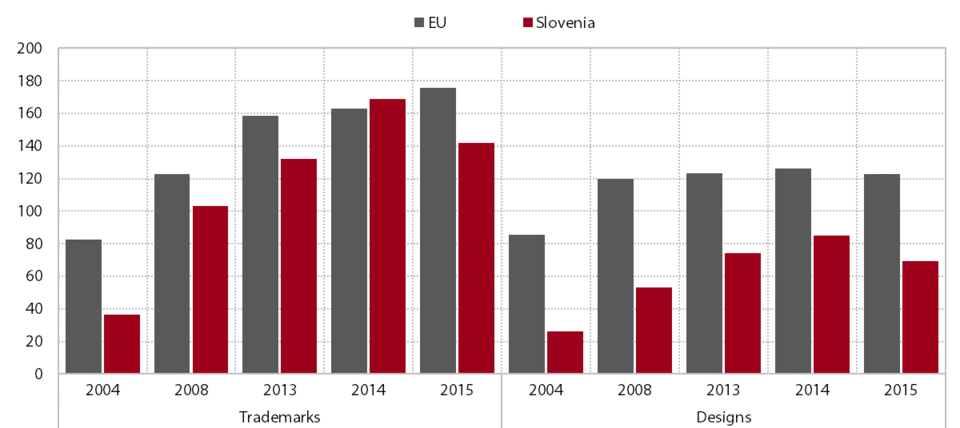
The number of patent applications with the European Patent Office (EPO) is lower than before the crisis, but some progress has been made in other areas of intellectual property protection, particularly Community trademark applications. According to data on the number of first patent applications filed with the EPO, Slovenian applicants have not yet reached the level recorded before the onset of the economic crisis, which is partly attributable to the structure of the economy since some sectors have more patentable subject matter than others. According to the international WIPO methodology, the patentable technological fields are as follows: medical technology, digital communication, computer technology and technology related to electrical machinery, apparatus and energy. Half of all the patent applications in 2010–2015 derived from these areas of technology (EPO Annual Report 2015, 2016). The business sector accounts for the largest share of patent applications by far, most of which are submitted by large companies (ibid). In 2009–2015 the number of patent applications per million population fell by an average of 1.0% per year in Slovenia, in contrast to the EU, where it rose at an average rate of 2.8%. Slovenia widened its gap with the EU average, but remained significantly more successful than the other countries in Eastern and Central Europe. Estonia and the Czech Republic, the countries with the best results in this group, reached only 40% of Slovenia’s performance in 2015. In 2009–2015 Slovenian applicants filed around 114 applications for Community trademark protection per million inhabitants per year with the OHIM, which corresponds to annual growth of 10.9%. Owing to the accelerated growth in applications for Community trademark protection in 2012–2014, Slovenia’s gap with the EU average narrowed significantly, from 36% in 2012 to 19% in 2015. In 2009–2015, Slovenian applicants registered around 72 Community designs per million population annually with the OHIM, which was 5.5% average annual growth. Slovenia’s gap with the EU average (122.6) remains significant.
Number of Community trademarks applications and registered Community designs per million population
16. Use of Internet and e-services
In terms of Internet usage and access to the Internet, the gap between Slovenia and the rest of the EU is gradually widening. Since 2010 the development of the information society has slowed significantly, causing the gap between Slovenia and the EU average to widen in terms of Internet users and households with online access. In recent years, Slovenia has also fallen behind many new EU Member States on these two indicators. Such developments can be partly attributed to the crisis, which made the Internet less accessible, particularly for more vulnerable population groups, but also to the lack of appropriate e-skills, particularly in specific population groups. Slovenia has therefore fallen even further behind the EU average in this period, especially with regard to Internet use among people in the first income quartile. Analysis of data by age and education reveals less favourable developments compared with the EU, particularly for less educated and older people, i.e. people who also often belong to more economically vulnerable population groups. Moreover, the data for these two population groups also reveal a significant lack of e-skills (basic skills for computer and Internet use) in comparison to the corresponding groups in the EU. The share of users from the highest income bracket has also stopped increasing in the recent period, but remains relatively high (over 90%) and slightly above the EU average. Regarding the use of newer technologies and the possibilities of using a wide range of e-services and mobile applications, it is encouraging to note that a large share of households have access to mobile broadband Internet (54%; EU 38%).
Slovenia also lags significantly behind the EU in the use of some advanced e-services. Internet users in Slovenia are on line to approximately the same extent as their counterparts in the EU for simple services such as searching for information, reading online news or downloading official forms. However, the gap between the EU and Slovenia is wide, and shows no signs of narrowing, not only in the use of some more sophisticated e-services, particularly online banking, social and professional networking, online shopping and the submission of completed forms to government institutions, but also in terms of sending e-mail. This is mainly attributable to Slovenian Internet users lacking the appropriate skills to do so. Data show that basic computer skills are fairly good, but Slovenia lags behind the EU regarding the advanced skills required to use more sophisticated e-services. In other factors that could impact the use of these services, such as access to the broadband Internet and trust in the safety of e-services, there are no major divergences from the EU. According to the Eurostat survey on Internet safety, only the share of respondents who refrained from online purchases for security reasons was somewhat higher than the EU average in 2015; the share of those who, for the same reasons, did not use e-banking was equal to the EU average, whereas the use of social networking sites and e-government services was less of an Internet safety concern in Slovenia than in the rest of the EU.
Internet users in the last three months, as a % of selected population, 2015
17. Trust in institutions
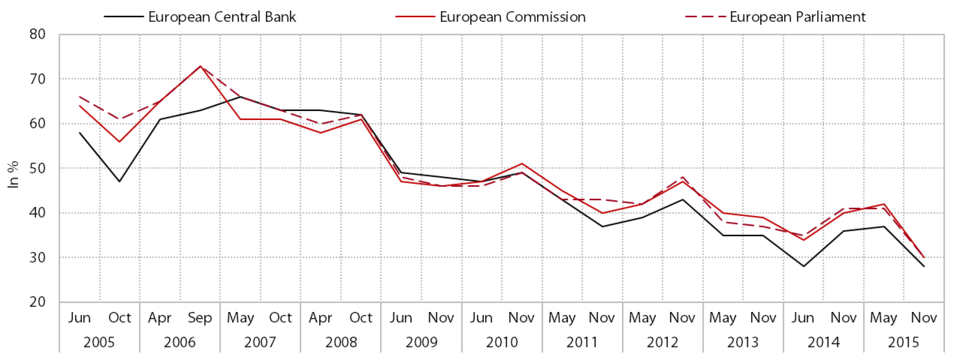
Trust in institutions remained low in Slovenia in 2015. Having declined significantly since the beginning of the crisis, it is now among the lowest in the EU. According to the latest survey, the proportion of respondents who trust the parliament and the government rose slightly compared with 2014, but is lower than the previous measurement taken (Standard Eurobarometer 83). Trust in local authorities declined and trust in political parties remained very low. Trust in the government and local authorities remains below the EU average, and trust in the parliament and political parties is among the lowest in the EU. The low trust in institutions is largely related to dissatisfaction with the current economic and general situation in Slovenia. The most recent Eurobarometer data show that respondents are still dissatisfied with the employment situation in Slovenia (91%), the situation of Slovenia’s economy (80%) and the quality of life in Slovenia (53%), but the share of respondents who perceive the current situation to be bad has declined in all these areas. The majority also expect things to remain generally the same over the next year.
Trust in the EU and its institutions has also declined. Compared with the measurements taken in spring 2015 (Eurobarometer 83) and the previous year, trust in the EU and its main institutions declined in the latest measurement and is at its lowest point in 12 years. In November 2015 the share of respondents who trusted the EU was 10 percentage points lower than one year earlier and below the EU average for the first time. In total 30% of respondents in Slovenia trust the EU parliament and the European Commission and slightly fewer trust the European Central Bank (28%); these figures are also below the EU average. The lower levels of trust can be attributed to the increase in the proportion of people who believe that things are heading in the wrong direction in the EU. This is mainly related to the extent of the refugee crisis in Europe, given that as many as 74% of respondents in Slovenia see immigration as the most important issue currently facing the EU. In contrast to previous years, a smaller proportion of respondents perceive the economic situation to be the EU’s main concern (19%), but more worry about terrorism (17%).
Trust in EU institutions, Slovenia, in %
1. Fertility rate and life expectancy
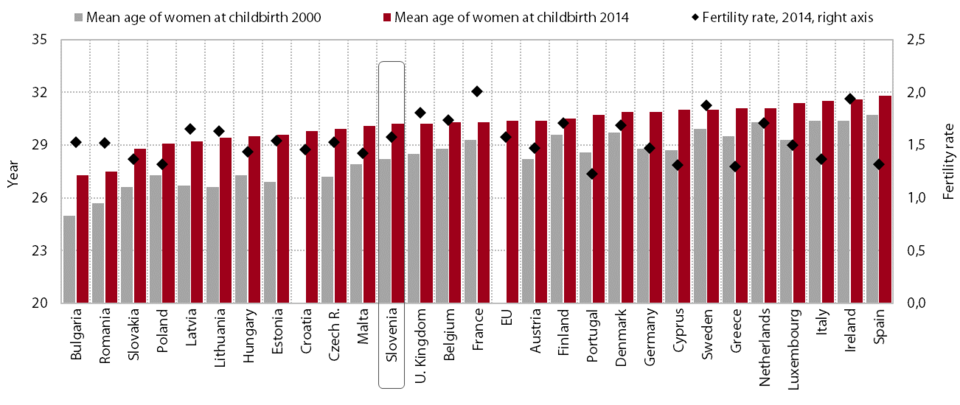
The fertility rate, which has hovered around 1.56 children per woman of childbearing age since 2008 (2014: 1.58), has been at the EU average for the last two years. No EU country has a fertility rate that would ensure even a simple replacement of the population (2.1), the countries coming closest to this figure being France, Ireland and Sweden. In Slovenia around 1,000 fewer children have been born in the last two years than the average for 2008–2012, not only because women are having children later but also due to a faster decline in the number of women of childbearing age (in 2014 by 6,500). Meanwhile, the mean age of mothers at childbirth continues to increase, by around one month per year. Judging by the size of the generations and assuming there is no change to current fertility rates or family policy (which is otherwise favourable by international comparison), we can infer that the number of births will also decline in the years to come.
In 2014 life expectancy in Slovenia increased more than in previous years and was at the EU average. A girl born in 2014 could expect to live 83.7 years (7 months longer than a girl born one year earlier) and a boy 78.0 years (one year longer). In the period 1987–2014 the gender gap narrowed by 2.3 years; life expectancy rose by 9.8 years for men and by 7.6 for women, which is attributable to advances in medicine, greater access to health services, a healthier lifestyle and better living conditions. In the last two years (2012 and 2013), life expectancy at birth was at the EU average (above the average for women and below for men); life expectancy at the age of 65 (EU: 19.8 years) was somewhat lower (at the EU average for women and below for men). Women aged 65 can be expected to live another 21.3 years and men another 17.2 years. The gap between men and women is wider than in the EU on both indicators, which means that there is room for improvement in improving the lifestyles of men.
Mean age of women at childbirth (2000 and 2012) and fertility rate in EU countries (2012)
2. Net migration
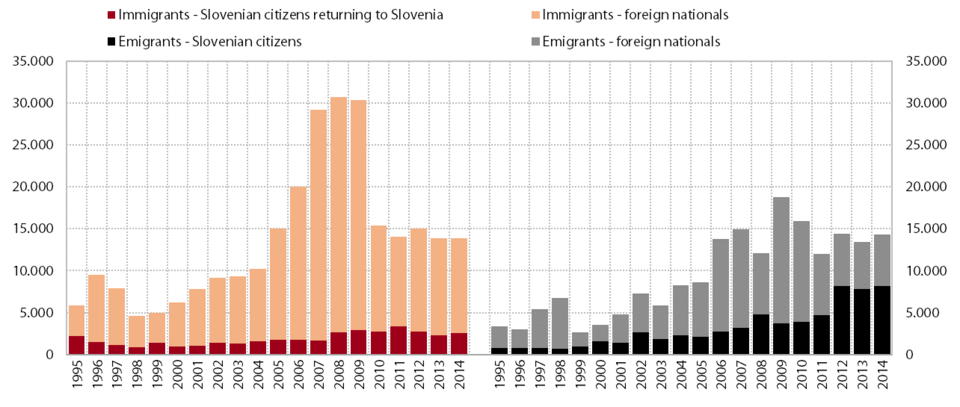
In the last few years total net migration has been low or negative in Slovenia, primarily owing to more Slovenian citizens emigrating from the country. Around 8,000 Slovenian citizens per year moved abroad in 2012–2014, resulting in a net migration figure of -5,500. In the last few years, Slovenian citizens already accounted for the majority (57.3%, on average) of all emigrants, i.e. citizens and foreign nationals together, compared with only 27.6% per year on average in the past (the average for the period 1995–2011). The negative net migration of citizens, a continuous trend since 2000, has therefore increased significantly in the last three years. The majority move to Austria and Germany (in 2014 almost half of all emigrated citizens), with around a tenth going outside Europe. Among the foreign nationals moving to Slovenia, the majority (approx. 70%), still come from the countries of the former Yugoslavia. Around 45% of foreigners move to Slovenia in order to find work, but family reunification has been almost as important a reason since 2011.
People emigrating from Slovenia are slightly older and better educated than those who immigrate. A total of 28.2% of emigrated citizens over 15 years old had completed at least higher education, which is the largest share in the four years since comparable data have been available; most settled in Germany and Austria (together 36.6%). Among the immigrated foreigners older than 15 years, only a good tenth had completed at least higher education and just over half had completed upper secondary education. Slightly less than 5% of all immigrated foreign nationals come to Slovenia to study. The average age of all the immigrants together is around 33 (of foreign nationals, 32), while the average age of the emigrants is 36 (of citizens, 37).
Emigration from and immigration to Slovenia
3. Age-dependency ratio
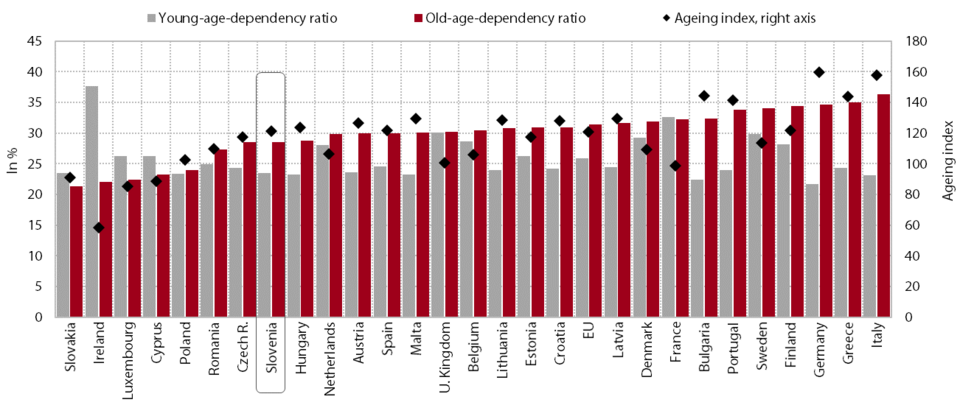
Owing to the declining number of working-age people and the growing number of older people, the age-dependency ratio has been rising more rapidly in recent years. Slovenia had 23.5 children and 28.5 older people (together 52.1) per 100 working-age population at the beginning of 2015. The number of older people (65+) is rapidly rising, not only as a result of gains in life expectancy, but also due to large post-war generations joining the ranks of the older population (65+). Given that the number of births was still at around 30,000 per year up to the early 1980s, this trend will also continue in the decades to come. At the same time, the smaller cohorts of people born in the 1990s (when the number of births per year was below 20,000) are entering the group of 20-year-olds (the working-age population). Since 2012 the number of working-age people (20–64 years old) has thus been falling. This means a decline in the potential active population, which will require the systems for the funding of social protection and the demand on the labour market to be adapted. With the current organisation of social protection systems, the declining working-age population and the increasing age-dependency ratio represent a growing problem for their financing. The old-age dependency coefficient in Slovenia is otherwise still below the EU average, but the gap is narrowing: according to EUROPOP2013 demographic projections, this coefficient will exceed the EU level by around 2022, which implies, among other things, increasing problems in financing ageing-related expenditure.
The ageing index for Slovenia shows that the number of older people has exceeded the number of children since 2004. The number of older people is rising much faster than the number of children. The number of people aged 80 and above is increasing particularly rapidly. In 2015 there were 21.4% more older people than children in Slovenia, which is an increase of 18.4 percentage points over 2004. The shares of older people and children in the total population rose to 17.9% and 14.8%, respectively, by 2015 (in 2004: 15.0% and 14.6%). People older than 80 years accounted for as much as 4.8% of the total population (in 2004: 2.9%). The parent support ratio, which shows the number of persons aged 85 years and over in relation to those between 50 and 64, is therefore also rising rapidly. In 2015, it was 9.7, compared with 4.5 in 1990. The increase in the share of the older population indicates the urgent need to adjust society, the environment and social systems to the larger number of older people.
The young-age-dependency ratio, the old-age-dependency ratio and the ageing index, 2015
4. Employment rate
Amid the ongoing economic recovery, the employment rate has been rising since 2013. Having exceeded the EU average before the crisis, it fell in 2009 after the decline in economic activity, and was below the EU average in 2012–2014. With the rebound in economic activity, it has risen in the last two years, returning to the EU average in 2015 (65.5%). During the crisis the employment rate declined slightly more for men, mainly owing to an above-average fall in activity in the construction sector and the low-technology manufacturing industries, both of which are dominated by male employees. The gap between the two employment rates therefore narrowed, but the rate for men remained higher than for women. Young people (15–20 years) were among those particularly affected by the crisis, and the employment rate for this demographic fell the most in the period from 2008 to 2013. However, this figure then rose more notably in 2015, partly due to the larger volume of student work, demographic trends and active employment policy programmes targeted at young people. The employment rate of older people (aged 55–64) remained higher in 2015 than in 2008, particularly as a result of the pension reform and the demographic effect of employed people entering the group of older workers, thereby increasing the employment rate for this group. Nevertheless, the employment rate for older people is still one of the lowest in the EU.
The employment rate of low-skilled workers has risen the most in the last two years under the impact of the structure of the recovery of economic activity. The employment rate of low-skilled workers fell the most in 2008–2013, owing to a significant decline in activity in construction and manufacturing, i.e. sectors that mainly employ a low-skilled labour force. As in other countries in the EU, the employment rate of those with higher education declined the least in the analysed period, mainly as a result of recruitment in public service activities and a smaller fall in activity in sectors that have a more educated workforce. In 2015 in particular the employment rate for low-skilled workers was up relative to 2013 (by 4.7 percentage points to 36.8%), owing – especially in the first year of recovery – to a notable increase in hiring through recruitment agencies, which usually provide labour for manufacturing, a sector in which most of the labour force has low, secondary and upper secondary education, and – in the last year – to a visible recovery in direct hiring in manufacturing.
Change in the employment rate by population group, between 2008 Q2 and 2013 Q2, and 2013 Q2 and 2015 Q2
5. Unemployment rate and long-term unemployment rate
With the continued economic recovery, the unemployment rate fell for the second year in succession, but remained twice as high as in 2008. Data from the labour force survey show that, after bottoming out in the third quarter of 2008 (4.1%), the unemployment rate had risen sharply by 2013 due to a decline in economic activity. With the recovery of economic activity, it then started to fall in 2013 (seasonally adjusted). By 2015 it had dropped by 1.2 percentage points (to 9.2%) and was lower than the EU average (9.5%), to which it had come fairly close during the crisis. At the onset of the crisis, the adverse effects on manufacturing and construction caused the unemployment rate for men to rise more than the unemployment rate for women. However, in 2012 the unemployment rate for women had nevertheless exceeded the rate for men again, and by 2015 the gap between the two widened slightly more. In the last two years, the unemployment rate for low-skilled people declined the most (by 4.5 percentage points to 13.7% in 2015), in line with the structure of growth in employment through recruitment agencies, which provide labour to the manufacturing sector; the unemployment rate for people with upper secondary and higher education remained more or less unchanged. Young people (aged 15–24) were hit hardest by the crisis, their unemployment rate having risen to 24.1% in 2008–2013, before dropping notably over the next two years and reaching 15.5% in 2015.
The long-term unemployment rate fell last year for the first time since the onset of the crisis but remains over two times higher than its lowest level in 2009. As a result of a prolonged period of weak labour demand, the long-term unemployment rate in Slovenia has risen sharply since 2009. After the modest increase in 2014, it fell to 4.7% in 2015. In 2009–2014 the rates for men and women increased by a similar extent: while the male rate rose particularly at the beginning of this period, the female rate increased steadily throughout the period. During the crisis the long-term unemployment rate for young people rose the most, but last year it dropped significantly and stood at 6.1%. Despite the 2015 decline, the share of long-term unemployed in total employment remains large (51.5%) and slightly above the EU average (49.4%).
Change in the unemployment rate by population group, between 2008 Q2 and 2015 Q2
6. Temporary and part-time employment
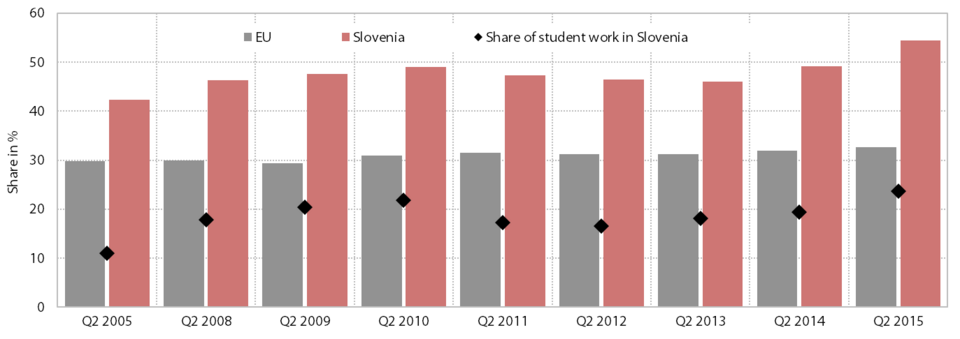
In 2015 the prevalence of temporary employment increased further. In the second quarter of 2015, the share of temporary employment in total employment stood at 17.8% (which is 1.3 percentage points more than in the second quarter of 2014) and was still higher than the EU average. The increase in the prevalence of temporary employment – despite the labour market reforms in 2013 which caused its share to decline in 2013 – is mainly related to employers’ caution in hiring and last year’s increase in student work. The share of temporary employment is still highest among young people (the 15–24 age group), ranking among the highest in the EU. Similar to other countries, temporary employment is more prevalent among women than men.
In 2015 the share of part-time employment in total employment remained similar to 2014, but higher than before the crisis. In the second quarter of 2015, it totalled 10.7%, 0.2 percentage points less than in the second quarter of 2014. In 2008–2015 it rose slightly more than in the EU as a whole which, in our view, was primarily a result of the greater significance of student work for total youth employment. Precisely owing to the prevalence of student work among young people (aged 15–24), the share of part-time employment is largest in this age group, where it is also significantly above the EU average.
Shares of temporary employment in total employment among young people aged 15–29 in Slovenia and the EU, and the share of student work in total youth employment
7. Minimum wage
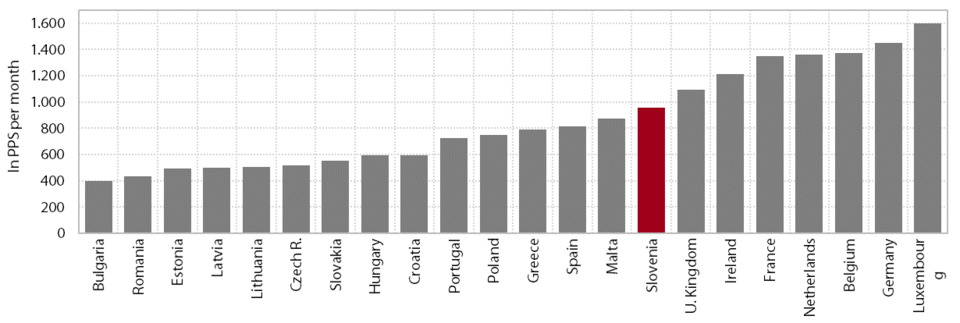
After increasing strongly in 2010–2013, growth in the minimum gross wage slowed over the last two years; the ratio of the minimum gross wage to the average wage has nevertheless risen significantly since the onset of the crisis. Because the crisis coincided with changes in legislation, the ratio increased to 50.8% (which is 10 percentage points more than in 2008), putting Slovenia at the top of the EU rankings. Throughout the crisis, minimum wage growth exceeded labour productivity growth in private sector activities, but lagged behind in the last two years. During the crisis, Slovenia recorded one of the largest declines in economic activity in the EU. At the same time, it was also the country with the largest real increase in the minimum wage (by almost 30%); in some countries, the minimum wage remained almost unchanged for several years and even declined in others in certain years. This increase impeded a more rapid adjustment of wages to the crisis in 2010–2012, weakened the cost competitiveness of the economy and increased unemployment. It also narrowed wage inequality, an area in which Slovenia had otherwise not diverged from the EU average, even before the crisis. At the end of 2015 the definition of the minimum wage was changed, and since 1 January 2016 the allowances for unfavourable working hours have been exempted from the minimum wage and paid separately. However, in order to really improve the material situation of minimum wage recipients, who often work unfavourable hours, it would also be necessary to adjust the tax treatment of minimum wages.
The number of minimum wage earners declined significantly with the recovery of the economy in 2015 (to 37,159), but remained almost twice as high as in the year before the new minimum wage act was passed (2009). With the increase in employment, the share of minimum-wage earners in total employment also dropped notably last year but remained at 6.2%, much larger than in 2009 (3.0%). The majority of workers receiving the minimum wage were still recorded in private sector activities, although in the last two years their number declined by a third to 28,259 (2009: 18,596). In the period 2009–2015 their share increased from 3.8% to 6.3% of all persons employed. Meanwhile, the increase in the otherwise small share of minimum wage earners in public service activities was much larger (from 0.3% to 5.7%). The doubling of the number in the last four years (to 8,900) was mainly due to cuts in public servants’ wages. Relative to 2009, the number of minimum wage earners rose the most in both relative and absolute terms in education, where it was 45-fold. In absolute terms, it also rose notably in the sectors of distributive trades and health and social care.
Minimum gross wage, July 2015, in PPS
8. Young people neither in employment nor in education or training
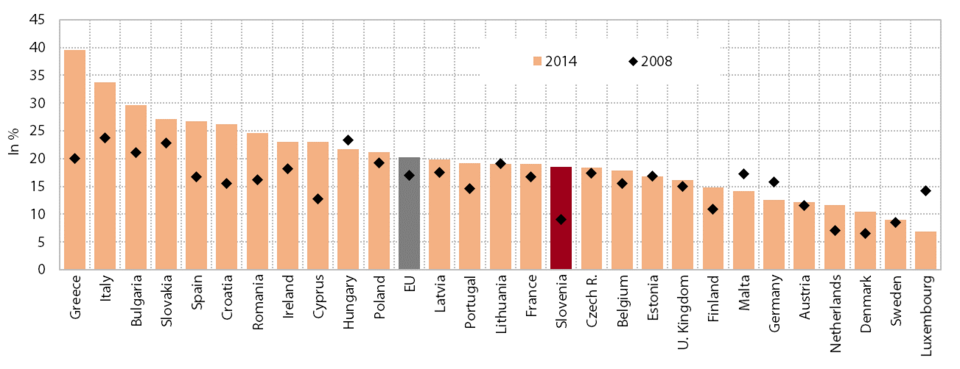
In 2008–2014 the share of young people neither in employment nor in education or training (the NEET rate) increased more in Slovenia than in the EU, but remained below the EU average. This is explained by the significantly higher participation of young people in upper secondary and tertiary education than the EU average. The NEET rate is therefore lowest in the 15–19 age group. In the 20–24 age group, the NEET rate is much higher, which is linked to the modest demand for young people (without experience) with completed upper secondary and tertiary education (the first cycle of Bologna study programmes), but is still lower than the EU average due to their high participation in tertiary education. In 2008–2014 the NEET rate for young people aged 25–29 rose the most, which is related to the increase in the number of tertiary graduates, the lack of jobs for these graduates and a skills mismatch. Despite the implementation of the Youth Guarantee schemes, the NEET rate in the 20–24 and 25–29 age groups did not change significantly in 2014, but the rate for the 30–34 age group continued to rise, which was, in addition to the modest demand for labour, partly due to active employment policy programmes and labour market intervention measures being targeted at those younger than 30. In the 20–24 age group, the female and male NEET rates are almost equal, but the NEET rate is significantly higher for women than men among those aged 25–29 and 30–34. It also increased more during the crisis. Women tend to face more problems in the transition from education into employment than men, which is attributable to worse employment prospects for young people graduating from social sciences, where women predominate, and restrictions on employment in the public sector, where women make up a larger share of the workforce than men.
Share of young people (25–29) neither in employment nor education or training, 2008 and 2014, in %
9. Social protection expenditure
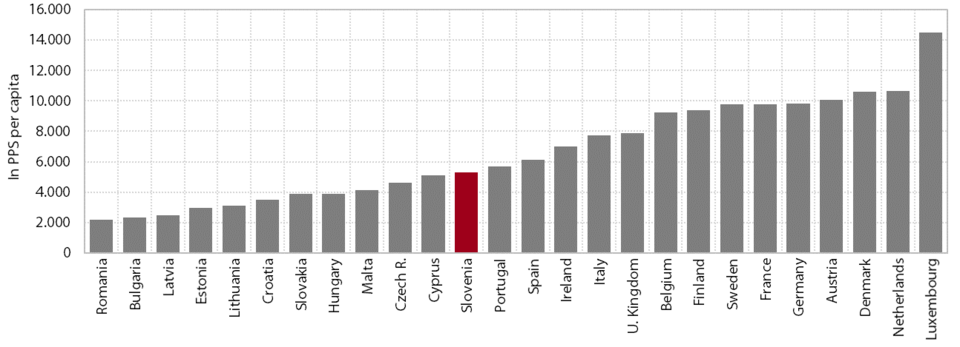
After a period of growth at the beginning of the crisis, social protection expenditure declined in 2012 and 2013. The decline was a consequence of changes to social legislation and fiscal consolidation measures, which entered into force in 2012. Expenditure growth during the crisis was attributable to deteriorating labour market conditions, mass retirements and the rising demand for health care and long-term care services. Among the major expenditures, expenditure related to old age, the category that accounts for the largest share of total social protection expenditure, expanded the most. Accelerated retirement before the implementation of the new pension legislation and the larger size of the retiring generation means the increase would have been even larger had the government not adopted measures to restrict the adjustment of pensions for inflation. Expenditure on sickness and health benefits also rose significantly.
In terms of social protection expenditure as a share of GDP, Slovenia lags behind the EU average, most notably in expenditure on unemployment benefits. Slovenia’s social protection system nevertheless provides relatively good access to health services and reduces the poverty risk. A comparison between expenditure on social protection in PPS in Slovenia and the EU average reveals that Slovenia lags the most behind the EU in terms of expenditure on unemployment, where it reaches only just over half of the average expenditure in the EU. This is due to a small share of unemployment benefit beneficiaries, which also appears to be the reason why the at-risk-of-poverty rate of unemployed people is much closer to the EU average than the at-risk-of-poverty rate for the entire population. Slovenia exceeds the EU average only in expenditure on social exclusion, which is – together with the effective targeting of beneficiaries – also likely to be the reason why social transfers are more effective at reducing the poverty risk in Slovenia than in the EU as a whole. The efficiency of our system is also corroborated by the fact that Slovenia spends much less on its management (management and administration costs and other expenses).
Social protection expenditure in PPS per capita, 2013
10. Health expenditure
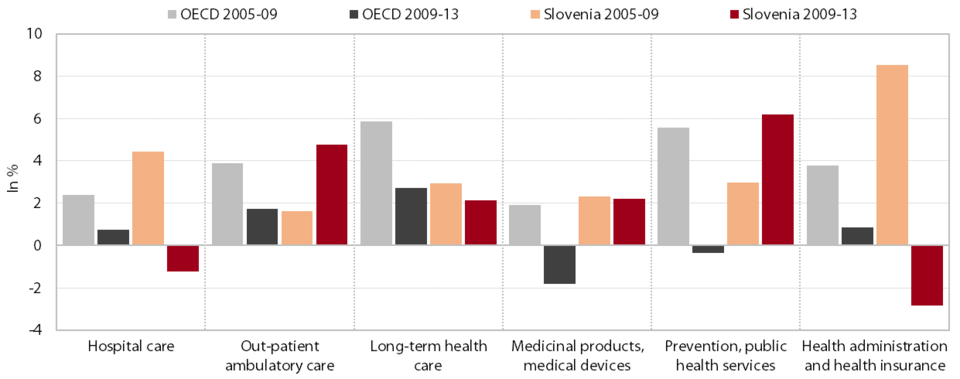
After a significant decline during the crisis, health expenditure rose in real terms in 2014 and 2015. According to the first estimate, current health expenditure (excluding capital formation) amounted to 8.5% of GDP in 2015 and 8.6% of GDP in 2014. Health expenditure is closely linked to HIIS revenue, as the HIIS is required to have a balanced budget and may not borrow or raise contribution rates. The higher revenue from contributions for compulsory health insurance in 2015 (by 3.3% in real terms) mainly stemmed from higher employment and earnings in the private sector and additional revenue from the increase in contributions levied on student work. Furthermore, most of the measures for balancing the HIIS budget that had been adopted during the crisis remained in force. After several years of austerity, in 2015, the HIIS was able to allocate these additional funds for the expansion and improved evaluation of some priority programmes (e.g. model practices, oncology, nursing homes, biological medicines), the reduction of waiting times and increased expenditure on sickness benefits. According to the first estimate, current public expenditure accounted for 6.1% of GDP in 2014 and 2015, while its share in total expenditure rose from 71.4% in 2014 to 71.9% in 2015.
During the crisis, health expenditure in relation to GDP surged, while per capita expenditure remained around the pre-crisis level. As in 2009–2013 GDP contracted more than in the EU as a whole, expenditure as a share of GDP rose at an above-average rate and was higher than the EU average. In 2013 current health expenditure accounted for 8.8% of GDP; total health expenditure, including capital formation, accounted for 9.1% of GDP (EU: 8.7% of GDP). In the period 2009–2013 current health expenditure per capita in PPS USD contracted by roughly the same extent as in the EU as a whole (by 0.3% per year in real terms). In 2013 it totalled PPS USD 2,511 (PPS EUR 2,163), which was 90.3% of the EU average (2008: 90.6%) or 73% of the OECD average (2008: 77%).
The measures taken during the crisis have contributed to a more efficient health expenditure structure. A comparison of the health expenditure movements by function shows a significant turn during the crisis, which was positive from the perspective of recommendations regarding the restructuring of health expenditure towards improving the efficiency of the system: growth in expenditure on out-patient ambulatory care strengthened; expenditure on hospital care declined; investment in prevention and public health surged; and expenditure on system administration declined notably. It is less encouraging to note that Slovenia is lagging further and further behind in the share of expenditure on long-term health care (SI: 10%; OECD: 12%), particularly community nursing and attendance allowances. While the majority of more advanced OECD countries had already intensified public funding for these services before the crisis, Slovenia still recorded below average growth in this expenditure during the crisis.
Real growth rates of health expenditure by function, per capita, Slovenia and the OECD, 2005–2009 and 2009–2013
11. Expenditure on long-term care
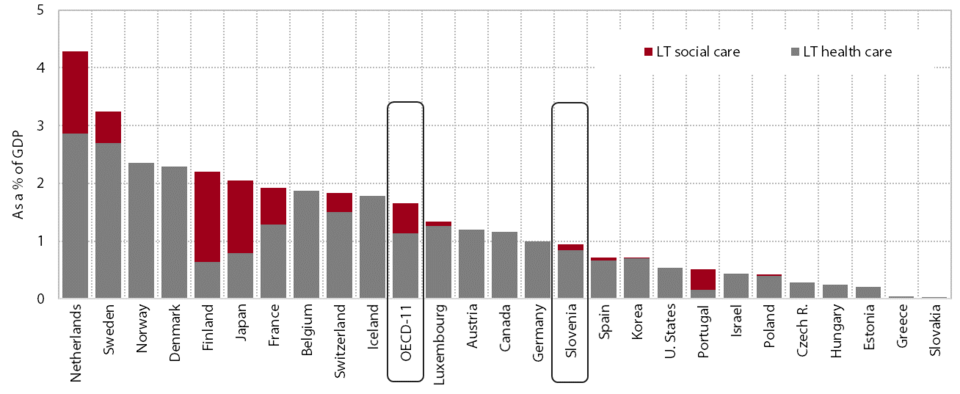
After increasing during the crisis, total expenditure on long-term care (LTC) declined in real terms in 2013. According to the latest data available, it also fell as a share of GDP and totalled 1.31% of GDP. Owing to austerity measures in the public sector, public expenditure on LTC declined by 2.9% in real terms in 2013; private expenditure on co-payments in institutions also decreased (−1.7%). Broken down by source of funding, the share of private expenditure increased again, to 27.5%; broken down by function of care, the share of expenditure on long-term social care was up to 33.3%.
Slovenia’s gap with the OECD average in terms of long-term care development is widening. In 2005–2013, public LTC expenditure rose by 2.2% per year in real terms in Slovenia and by an average of 0.4% in the OECD (OECD Health at a Glance 2015). In terms of public LTC expenditure (0.95% of GDP), Slovenia is lagging further and further behind the OECD average (2013: 1.66% of GDP). There is a wide gap in the share of long-term health care services (SI: 0.8% of GDP; OECD: 1.1% of GDP; these mainly include community nursing, nursing allowances and institutional health care) and an even wider gap in long-term social services (SI: 0.1% of GDP; OECD: 0.5% of GDP: particularly social care at home). While more advanced OECD countries primarily increase public funding for long-term care at home, the ratio in Slovenia is the opposite, as Slovenia increases funding for institutional care rather than care at home. As in 2013 as much as 77.7% of expenditure was allocated for long-term care in institutions (retirement homes, special social welfare institutions, hospitals) and only 22.3% for long-term care at home, the comprehensive systemic regulation of LTC funding must be devised as soon as possible.
Public expenditure on long-term (health and social) care as a share of GDP, 2013
12. Pension expenditure
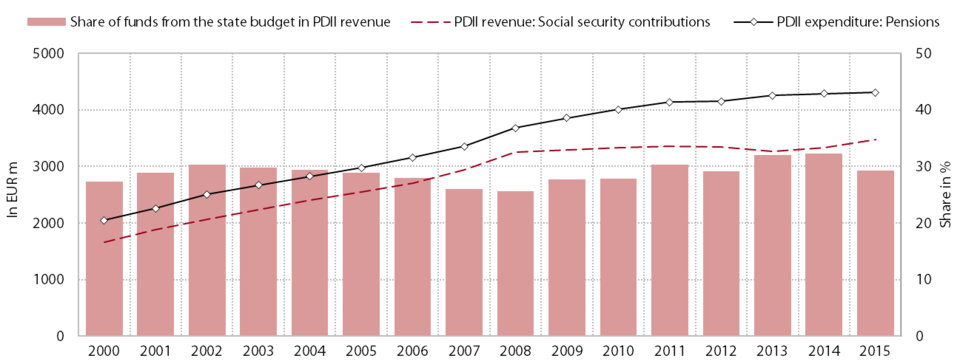
Pension expenditure increased further in 2015 and the budget transfer to the pension fund also remains high. Pension expenditure, including the annual pension allowance, totalled EUR 4.305 billion and was up 0.4% (expenditure excluding the annual allowance was at the level of 2014). In 2015 there was once again no indexation of pensions. The number of old-age pensioners expanded less than in previous years (a net increase of 5,800, which is nearly three times less than the average for 2010–2013) because the transition periods (the last one will expire in 2020) have caused the retirement conditions to be tightened from year to year as the provisions of the pension reform become fully applicable. Expenditure on the annual allowance was higher, with the limit for annual allowance entitlement raised from the pension amount of EUR 622 to EUR 750, this increase being financed by funds received from Kapitalska Družba (EUR 19 million). The budget transfer stood at EUR 1.482 billion, which is less than in the previous two years, but still accounts for 29.3% of PDII revenue.
Pension expenditure as a share of GDP in Slovenia is still below the EU average, but is rising faster than in the EU due to the rapid ageing of the population. According to the most recent data available, pension expenditure as a share of GDP remained below the EU average in 2012. While in the EU it was 1.2 percentage points higher than in 2008, it was as much as 1.9 percentage points higher in Slovenia. Pension expenditure is expected to stabilise over the medium term due to the ZPIZ-2 (The Pension and Disability Insurance Act), before starting to rise again in 2023 and reaching the 2013 level by 2028. This means that the new pension system does not ensure long-term fiscal sustainability; in contrast, pension expenditure for the EU as a whole is also projected to stay at the current level in the long term.
Selected PDII revenues and expenditures, Slovenia
13. Gross adjusted disposable income per capita
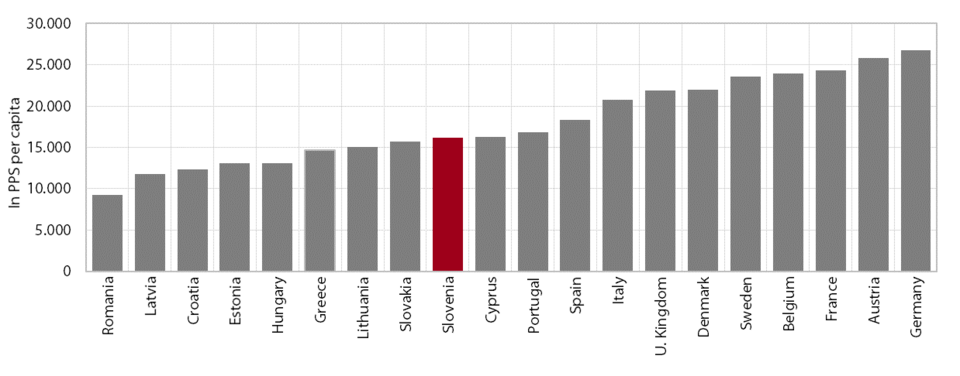
Gross adjusted disposable income per capita rose in 2014 after the slowdown in its growth at the onset of the crisis and a decline in 2012 and 2013. At the beginning of the crisis the growth of gross disposable income slowed as a consequence of a larger decline in economic activity and a steeper fall in employment than the EU average. In 2012 and 2013 gross adjusted disposable income contracted, not only owing to lower employment and wages but also due to austerity measures in the area of social transfers. With the improvement in labour market conditions, gross adjusted disposable income increased in 2014. In relation to the EU, Slovenia reached the highest level of gross disposable income per capita in PPS in 2008, 83.5%, which was a wider gap than in economic development as measured by GDP in PPS (89% of the EU average). With the economic crisis and fiscal consolidation measures, Slovenia’s gap in disposable income had risen to 22 percentage points by 2014 (the latest figure available), which is a 5-percentage-point wider gap than that for economic development (see indicator 2.1).
The structure of disposable income shows that Slovenian households earn more income from employment and less from property than the average EU household. Owing to the deterioration in labour market conditions, in 2008–2014 the share of income from employment (compensation of employees) declined slightly more in Slovenia than the EU average, but remained larger. The share of social transfers does not differ significantly from the EU average. Its increase during the crisis was also similar to that in the EU. On the other hand, Slovenia diverges significantly from the EU average in terms of its share of income from property (in 2014 this share totalled 2.3% in Slovenia and an average of 12.2% in the EU).
Gross adjusted disposable income of households and NPISHs in PPS per capita in Slovenia and selected EU countries, in 2014
14. Actual individual consumption per capita
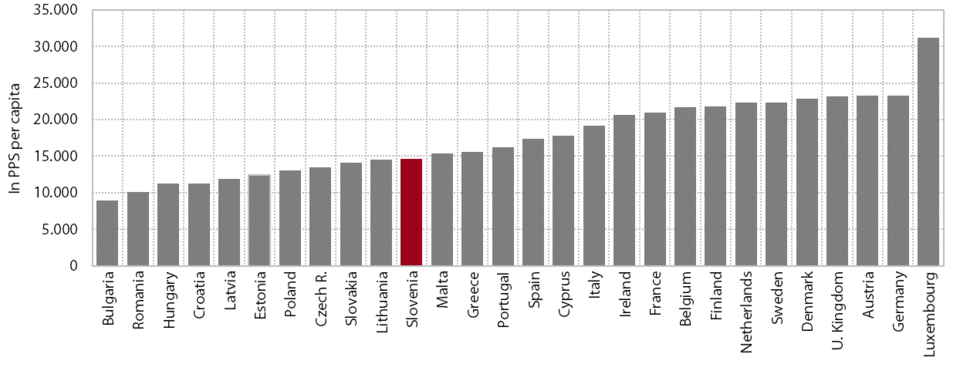
After the moderation of its growth at the onset of the crisis and a decline in 2012 and 2013, actual individual consumption per capita stopped falling in 2014. After the rapid growth in the pre-crisis period, its growth eased significantly at the beginning of the crisis. We estimate that, in the first years of the crisis, the decline in consumption was prevented primarily by wage growth in 2008–2010 as a result of the introduction of the new system for public sector wages and the increase in the minimum wage. The decline in individual consumption in 2012 and 2013 was, in our view, due to the contraction in government consumption and a fall in household disposable income owing to falling employment and wages. With the recovery of economic activity and an increase in disposable income, actual individual consumption stopped falling in 2014.
Slovenia has widened its gap in individual consumption per capita in PPS in relation to the EU average since 2010. Despite the contraction in economic activity and employment, the modest growth in disposable income at the beginning of the crisis helped individual consumption stay at the level achieved. In 2011 individual consumption reached 80.2% of the EU average, which is a slightly wider gap than in the measure of economic development (GDP per capita, see indicator 2.1). Slovenia’s divergence from the EU average since 2011 reflected the urgently needed austerity measures in the public sector, which reduced expenditure on social transfers in kind and average earnings in 2012 and 2013. Despite GDP growth and modest growth in individual consumption in 2014, individual consumption per capita in PPS moved further away from the EU average to 75.7%.
Actual individual consumption per capita in PPS, in 2014
15. Income inequality
Despite the increase in income inequality indictors in 2008–2014, Slovenia is one of the countries with the lowest income inequality rates in the EU. Slovenia has the second lowest rate of income inequality in Europe as measured by the Gini coefficient, and the third lowest rate as measured by the quintile share ratio (80/20). In 2014 the Gini coefficient rose by 0.6 percentage points to 25% while income inequality as measured by the income quintile share ratio (80/20) increased by 0.1 percentage points to 3.7. In the period 2008–2014 the Gini coefficient was up 1.6 percentage points and the income quintile ratio was up 0.3 percentage points.
The increase in income inequality during the crisis was attributable to a decline in income in lower income brackets. It reflected the economic crisis, fiscal consolidation measures and changes to social legislation implemented in 2012. Since 2007, the share of income per family member in the lowest quintile had decreased by 0.8 percentage points, while the corresponding share in the highest quintile had increased by 1.0 percentage points. Regarding the deciles, the bottom income deciles experienced the largest decline and the top income deciles the largest increase in income during the crisis.
Income inequality indicators, Gini and 80/20, 2014
16. Life satisfaction
In autumn 2015, life satisfaction in Slovenia exceeded the long-term average for the first time in six years, approaching the levels seen before the crisis. According to the Standard Eurobarometer survey, Slovenians have been more satisfied with their lives than people in the EU as a whole in all the years of measurement; however, the EU average had already exceeded its long-term average in spring 2014. General life satisfaction is still highest in the northern EU Member States. The results of the autumn 2015 measurement already reflect the consequences of migration pressures.
In autumn 2015 satisfaction increased in all four areas measured by the Eurobarometer: household financial situation, personal employment situation, and employment and economic situation in the country. Slovenian respondents are still the most satisfied with the financial situation of their households (64%), where in autumn 2015 satisfaction also exceeded the level seen before the crisis. They are the least satisfied with the employment situation in the country (7%). On the other hand, their optimistic expectations dropped in all areas except the personal employment situation.
In the results of the autumn 2015 survey, the issue of migration stands out and has probably also affected evaluations of satisfaction. Migration may partly explain the relatively significant increase in the level of life satisfaction in Slovenia: on the basis of their own experiences with migration or seeing pictures of migrants, people may have adjusted their expectations and criteria for evaluating life satisfaction and are more satisfied with what that have (crisis adaptation), as what until recently has been seen as the main problem now appears less acute. When asked about the two most important issues currently facing the country, respondents stressed immigration as the main problem (48% of respondents), which has therefore overtaken unemployment (41%) and the economic situation (27%), the issues that had previously been seen as the main concerns. In evaluations of the main issues at the personal level there were no significant changes in the last measurement.
Life satisfaction, in %
17. Healthy life years
People in Slovenia can expect slightly more than 58 years of healthy life, which is significantly below the EU average, but the gap has been closing despite the crisis. According to the latest data available, a girl born in 2013 can expect 59.5 years of healthy life, while a boy can expect 57.6 years. Despite the crisis, the number of expected healthy life years rose significantly in Slovenia in 2013 and the gap in relation to the EU narrowed slightly. However, this indicator is derived from subjective perceptions of limitations in daily living and so the results may also reflect the greater sensitivity of the population in evaluating their own situation.
The ratio of life expectancy to the number of healthy life years has improved in the last years but remains one of the lowest in the EU. People in Slovenia spend only 73% of their lives free from any limitation (in the EU: 76%), which leads to early retirement and increased expenditure on health and long-term care. The narrowing of the gap between life expectancy and the number of healthy life years would significantly contribute to slower growth in health spending in the future and, in turn, to the sustainable financing of health and long-term care in the long term.
Slovenia is also narrowing its gap with the EU average as regards expected healthy life years at the age of 65. In Slovenia a person aged 65 can expect to live another 7.4 years in a healthy state, compared with 8.6 years in the EU. A few years ago the gap was much wider. During the crisis the number of healthy life years at the age of 65 rose slightly in Slovenia but declined on average in the EU. The favourable movement of this indicator in Slovenia is in all likelihood the result of successful preventive health care programmes for elderly people and the relatively high level of access to health services, which was also preserved during the crisis (see section 3.2).
Ratio of life expectancy to the number of healthy life years, 2013, in %
18. Share of population with at least upper secondary education
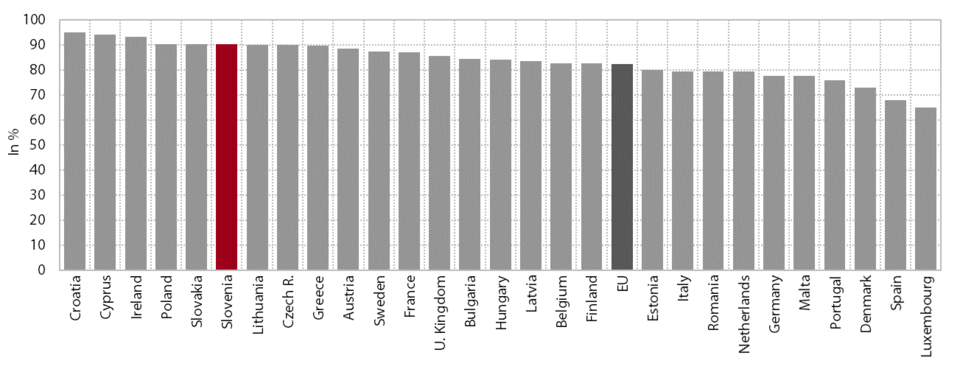
Slovenia has a relatively large share of adults aged 25–64 years with at least upper secondary education, and this figure is rising further. According to the labour force survey (for the second quarter), it stood at 86.5% in 2015, which is higher than the EU average. In the last ten years, it rose the most in the middle-age (45–54 year olds) and the oldest age (55–64 year olds) groups, which is linked to the transition of younger, more educated populations into higher age groups. The share of adults aged 25–64 years with at least upper secondary education is above the EU average in all age groups. The share of the population with at least upper secondary education is higher for men than women, although the gender gap has narrowed in the last decade.
The share of young people (20–24 years) with at least upper secondary education has remained more or less unchanged in the last ten years. In 2015 it was almost the same as one year previously and higher than the EU average (Slovenia: 90.1%; EU: 82.3%). This large share is related to the high participation of young people (15–19) in upper secondary education, which has hovered around 78% for several years and is above the EU average. The financial accessibility of upper secondary education increased in 2014 thanks to the reintroduction of state scholarships for underage pupils. The share of early school-leavers rose to 4.4% in 2015, but was below both the EU average (11.1%) and the national target (5.0%). The share of young people with at least upper secondary education remained roughly the same throughout the crisis, which is also expected to continue in the future. There is nevertheless still some room for improvement in the share of men, which is lower than for the corresponding share of women, also owing to a much larger share of early school-leavers.
Share of young people (20–24 years) with at least upper secondary education, 2nd quarter, 2015, in %
19. At-risk-of-poverty rate
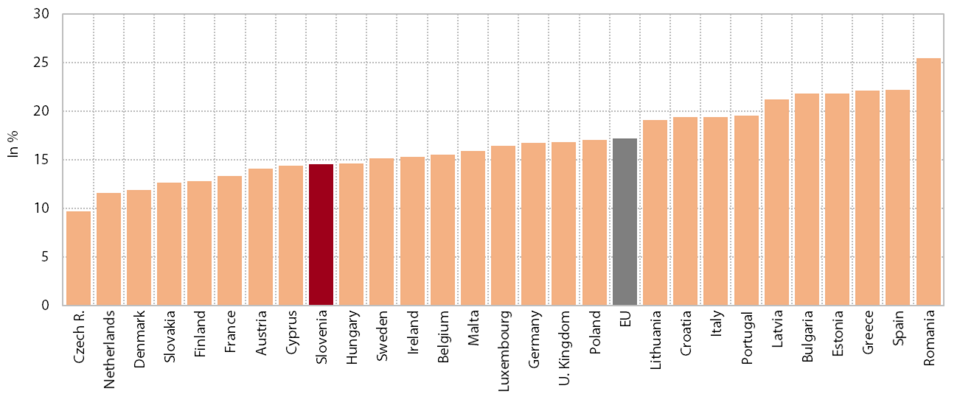
In 2014 the at-risk-of-poverty rate in Slovenia remained the highest in the last ten years, albeit still lower than the EU average. In 2014 it remained the same as in the previous year (14.5% or around 290,000 persons). It declined slightly for the most vulnerable population groups (households with children, one-person households older than 65, unemployed people), in our estimation due to changes to social and pension legislation. The at-risk-of poverty rate increased the most for one-person households younger than 65. In terms of activity status, the risk of poverty increased only in the ‘other inactive persons’ group, which we estimate was also due to the more restrictive eligibility criteria for social assistance after the social legislation reform entered into force.
The relative at-risk-of-poverty gap thus rose from 20.2% to 22.0% in comparison with the previous year and was the widest since the beginning of the crisis. The median income of people below the poverty threshold declined by another EUR 7. The at-risk-of-poverty threshold rose by EUR 3 per month owing to a slight increase in the average household disposable income.
At-risk-of-poverty rate, 2014
20. Material deprivation
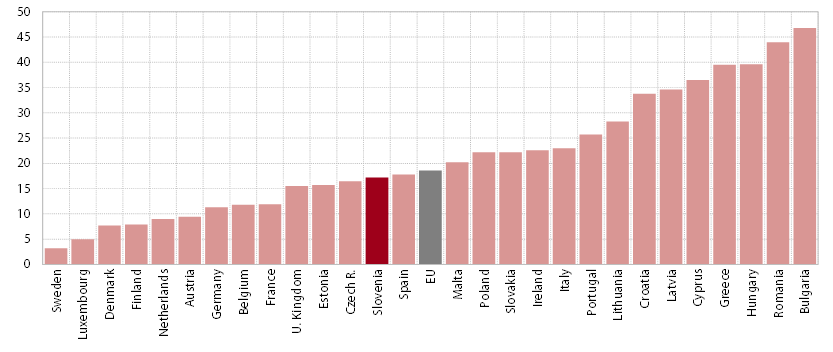
The material deprivation rate (i.e. deprivation in at least three of the nine items ) rose slightly in Slovenia in 2014. In 2014 it increased by 0.2 percentage points to 17.2%, but was still lower than the EU average (18.6%). The share of materially deprived people was significantly higher among those living below the at-risk-of-poverty threshold (45%), up 1.8 percentage points over one year earlier. The severe material deprivation rate (i.e. deprivation in four of the nine items) in 2014 was somewhat lower than in 2013.
The shares of households that cannot afford a car (4.3%) and have difficulty paying housing-related bills (22.5%) were higher in 2014 than in 2013 and the highest in ten years. The shares of those who cannot keep their home adequately warm or afford a one-week annual holiday away from home were also higher than for the previous year, but had been even higher during the crisis. The share of those who cannot afford a meal with meat, or a vegetarian equivalent, was the lowest in ten years at 7.9%. The shares of people unable to afford durable goods of small value and to deal with unexpected expenses remain at the previous year’s level (45.8%), which is 4.2 percentage points higher than in 2007. Almost all households can afford a telephone, a colour TV and a washing machine, their shares equalling those in 2008.
Material deprivation, 2014
1. Greenhouse gas emissions
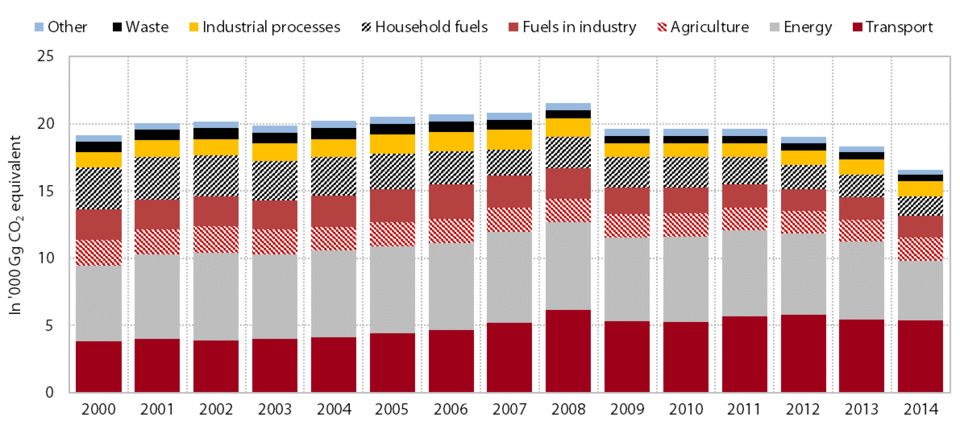
After declining with the onset of the crisis, greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions have continued to fall since 2011. According to the ARSO estimate, total GHG emissions amounted to around 16,600 Gg of CO2 equivalent in 2014, which was approximately 23% less than their peak in 2008 and around one-tenth less than in 2013. Since the beginning of the crisis, GHG emissions have declined in all eight source categories, but the most in the energy and transportation sectors, which account for the majority of emissions, and in the consumption of fuels in industry and households. The significant decline in the energy sector, where emissions are almost entirely due to electricity generation in thermal power plants, mainly stemmed from the shut-down of the biggest plant. The top position in terms of emissions is now occupied by the transport sector. Its emissions declined too, but are still fairly high by international standards, owing in part to the relatively favourable competitive conditions established through tax policies (the refund of excise duties) and strong merchandise flows through Slovenia. Emissions from the consumption of household fuels also declined in 2014, which could be attributed to the milder weather conditions; emissions from waste were also lower, as were emissions from other sources. Meanwhile, emissions were up in agriculture. Emissions from industrial processes also rose slightly again, but since their share was modest, they had a relatively minor impact on the quantity of total emissions. The main component of GHG emissions is carbon dioxide, which is generated mostly by the combustion of fuels; this is followed by methane and dinitrogen monoxide, which derive mostly from agriculture and landfilled waste.
Emission intensity is also declining, but was nevertheless relatively high until 2013 by international standards. GHG emissions fell considerably during the economic crisis owing to a steep decline in GDP, and this moved Slovenia much closer to meeting its international commitments. Nevertheless, with the emission intensity in the EU improving faster than in Slovenia, the gap has been widening. In 2013 Slovenia thus generated around 25% more emissions per unit of GDP than the EU as a whole, compared with 14% more in 2000. In 2014 GHG emissions fell significantly, whereas GDP at constant prices rose, which significantly improved the emission intensity of the economy.
GHG emissions by emission source category, Slovenia
2. Energy efficiency

Despite the decline in primary energy consumption, energy intensity has remained relatively high in recent years. One of the targets of the EU climate and energy package for 2020 is a 20% reduction in energy consumption with regard to the anticipated consumption according to the baseline scenario, with no additional measures. The Member States set their national unbinding targets according to their own scenarios. Three quarters of EU countries are required to reduce their energy consumption by 2020, while some, including Slovenia, are required to limit an anticipated strong increase. As EU Member States are well on track to meet their 2020 targets, more ambitious goals have already been set for 2030. The decline in energy consumption in Slovenia mainly reflected the weak economic activity, alongside the climate changes in the past two years, with higher annual temperatures and lower consumption of energy for heating. The decline in energy consumption is impeded by the high energy consumption in transport. Having mostly converged towards the EU average until 2007, energy intensity in Slovenia has since been falling more slowly. In 2014 it was a quarter higher than the EU average.
Final energy consumption in Slovenia is significantly affected by strong energy consumption in transport and, in recent years, lower consumption of energy for heating. In the period 2005–2014 final energy consumption fell twice as slowly in Slovenia than in the EU. The energy consumed by industry fell faster, but the improvement was cancelled out by higher energy consumption in transport, which was mainly attributable to increasing freight transit through Slovenia. Annual fluctuations were, in addition to economic activity, also influenced by excise policy. The decline in household consumption of energy for heating in the past few years has been attributable primarily to the installation of heat distribution systems in multi-dwelling houses and increasingly efficient heating appliances; the steep fall in 2014 was also due to the unusually warm weather during the heating season.
Final energy consumption by consumer sector in Slovenia and the EU
3. Emission-intensive industries
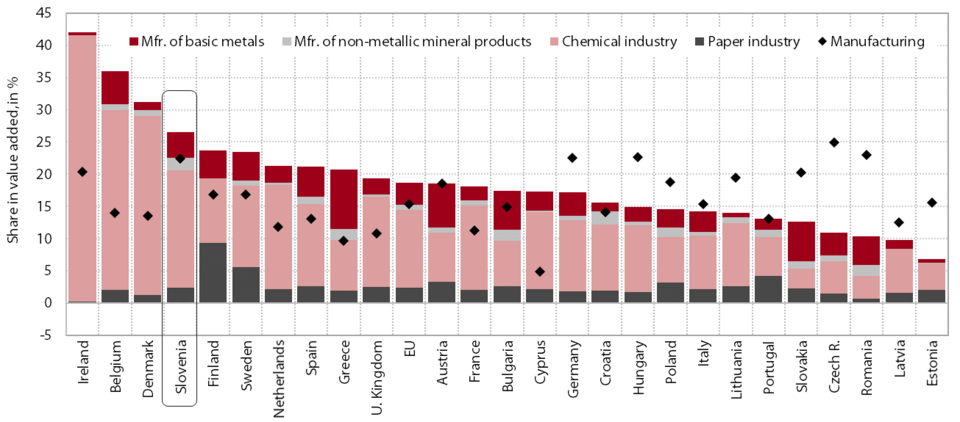
In the last few years, the total output in emission-intensive industries in Slovenia mostly grew faster on average than in other manufacturing industries. This trend was interrupted in 2008 and 2009, primarily as a result of the lower output in the manufacture of basic metals, and then in 2014, mainly owing to the more modest output in the chemical industry. In the last five years under observation, emission-intensive industries generated around a quarter of the total value added in manufacturing, which is one of the largest shares in the EU. Given the greater significance of emission-intensive industries and the higher energy intensity in manufacturing in Slovenia than in the EU as a whole, the impact of emissions trading on production costs and, consequently, business results and competitiveness is also greater than in the EU. In order to reduce exposure to higher costs, it is therefore crucial that Slovenia continues to reduce its energy intensity and proceed with technological restructuring in its emission- and energy-intensive industries.
The share of emission-intensive industries in manufacturing and the share of manufacturing in the value added of the economy, 2013.
4. Renewable energy sources
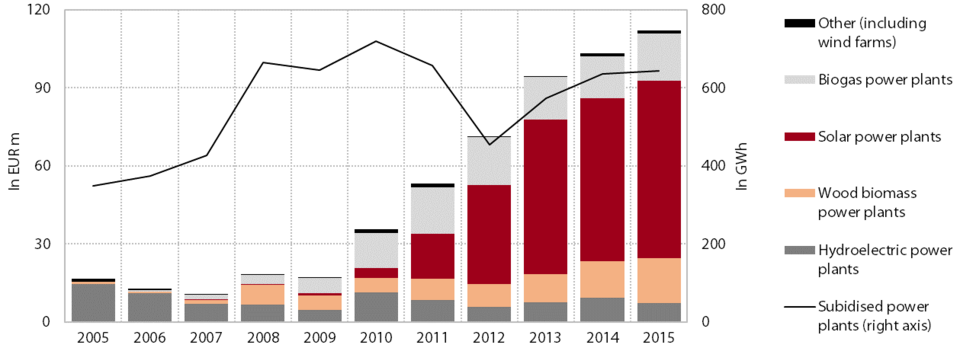
The share of renewable energy sources (RES) in final energy consumption is higher than the EU average, but is increasing slightly more slowly in the long term than in the EU. In Slovenia it increased more noticeably particularly in 2009, when final energy consumption fell by almost one-tenth because of the crisis, while the consumption of RES increased by around one-fifth. Since then, growth has slowed significantly. In 2014 final energy consumption fell owing to the warm weather during the heating season; the consumption of RES for heating declined even more. The share of RES thus dropped somewhat that year. According to our estimates, final energy consumption did not change significantly in 2015. The consumption of RES also stagnated, reflecting lower production in hydroelectric power plants, above-average temperatures during the heating season and lower consumption of liquid fuels.
The share of RES in heating in Slovenia is twice as high as the EU average, with a higher share in electricity and a lower share in transport. As in the EU, the most widely used source of renewable energy for heating is wood, while the main renewable energy source for electricity production is hydropower. The share of energy from other renewable energy sources was also relatively low in Slovenia in 2014 (12%) compared with the EU, where this share was three times higher, owing partly to the intense exploitation of wind energy. This is also the main difference in their RES structures. Slovenia is also in the bottom quarter of EU countries (and far from the targets set) in terms of its share of RES in transport. In the last ten years, the use of RES in Slovenia increased by almost 30%, mainly on account of wood, biofuels and solar energy, which contributed 39 percentage points, 18 percentage points and 14 percentage points to growth, respectively.
The amount of RES grants has been rising in recent years, particularly in the production of solar energy. In 2005 a total of EUR 16 million was devoted to grants for promoting electricity generation from RES, the bulk of which was intended for hydroelectric power plants. Since 2010 the amount of RES grants has been strongly rising, exceeding EUR 110 million in 2015, when the largest amount was allocated for solar power plants. With a shift towards more expensive energy sources, the amount of grants per unit of power generated from RES increased several fold.
Funds disbursed to support electricity production from RES, Slovenia
5. Road freight transport
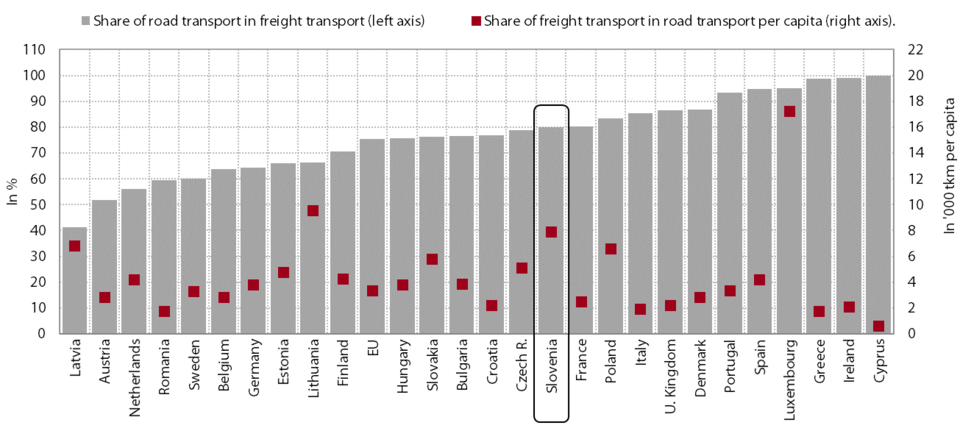
After declining since 2009, the share of road freight transport increased in 2015 and remained well above the EU average. In the EU it stagnated in the middle of the last decade, while in Slovenia it had been rapidly rising, so that Slovenia exceeded the EU average in 2005 and maintained a gap of around 6 percentage points as of 2009, before narrowing it slightly in 2014. In 2015 the number of tonne-kilometres performed by domestic hauliers increased significantly year-on-year, by 10%; the volume of rail transport rose considerably less in the same period, by around 2%. The share of road freight transport in total freight transport thus overshot 81% again. The volume of road freight transport exceeded the pre-crisis level by around one-tenth and the volume of rail freight transport by around 19%. From a sustainable development perspective, faster restructuring in favour of rail transport would be necessary, which would be best achieved through the implementation of railway infrastructure projects.
Slovenia has one of the largest freight transport volumes per capita in the EU, primarily owing to its transit location and the density of its transport infrastructure. Freight transport by domestic hauliers increased particularly significantly in 2003–2008. In 2014 domestic hauliers transported 2.3 times the amount of tonne-kilometres of freight per inhabitant transported by average hauliers in the EU. This increase is attributable to Slovenia’s location at the crossing of the V and X pan-European transport corridors (where transport also expanded with the enlargement of the EU) and a highly developed motorway network, the largest in the EU in per capita terms. Slovenia also has a relatively high level of freight transport by rail where, alongside the extensive railway network, the connection with the port of Koper also plays a significant role with around 60% of freight transhipped in Koper transported by rail.
Slovenian hauliers perform more and more of their services abroad, while the share of freight transported by foreign hauliers on Slovenian roads is rising. This trend also continued after 2008. In the period 2008–2014 the total distance of journeys made by Slovenian hauliers declined by more than 5%; the distance of journeys performed in the territory of Slovenia by all hauliers dropped by around 7%. Within that, the distance of journeys performed by Slovenian hauliers (solely) abroad increased by 26%, while the journeys made in the national territory and those at least partly connected to the territory of Slovenia (i.e. when goods are loaded or unloaded in Slovenia) declined by 16%. This means that transport by foreign hauliers on Slovenian roads expanded, which is also confirmed by data on the number of passages through toll stations, according to which the share of foreign freight vehicles on Slovenian motorways rose by 15 percentage points to 68% in 2008–2012.
Road freight transport in Slovenia and the EU
6. Waste
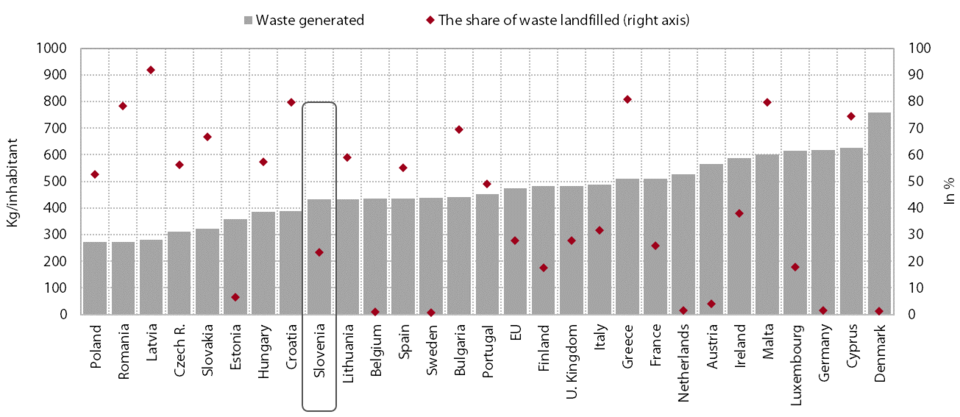
Having declined during the crisis, waste generation increased in 2013 and 2014. In 2014 approximately 4.7 million tonnes of different types of waste was generated in Slovenia, around 5% more than in 2012.1Opomba je spodaj, označena z zeleno. One fifth was municipal waste, i.e. waste from households and other waste of similar origin managed by the providers of mandatory local public services for environmental protection. After rising by about 15% in 2013, municipal waste increased by another 5% in 2014. The quantity of separately collected municipal waste, which is rising in the long term, increased to 65% of total waste generated. The other four-fifths was waste from production and service activities. After declining significantly at the onset of the crisis, the quantity of this waste has increased slightly since 2012. The vast majority of waste, around nine-tenths, was generated in four sectors: (i) manufacturing; (ii) construction; (iii) water supply, sewerage, waste management and remediation activities; and (iv) electricity, gas and steam supply.
Waste management continues to improve. The total quantity of waste recovered in 2014 amounted close to 6.1 million tonnes; after two years of decline, this was roughly the same as in 2010 and 2011. The actual amount recovered (excluding pre-treatment or removal and backfilling) was approximately 50% lower. Recycling, a very desirable form of recovery from an environmental perspective, amounted to nearly 2.7 million tonnes, which is 44% of total recovery. Landfilling is the least favoured option in the waste management hierarchy. The quantity of landfilled waste amounted to around 283,000 tonnes, almost one-tenth less than in 2013 and around 5% of the total amount recovered. The share of landfilled municipal waste decreased again, totalling around one-quarter in 2014, as two-thirds of municipal waste was already collected separately and as residual mixed municipal waste must be treated before going to landfill.
In terms of municipal waste generation, Slovenia performs better than the EU. In 2014 a total of 43 kg of municipal waste per person was generated in Slovenia, which is 9% less than the EU average. Compared with the EU, a larger share of municipal waste was recycled and a smaller share was landfilled; however, at the same time, a relatively large amount of waste remained in treatment (the “other treatment” category). In the EU, as many as six EU Member States have already reduced their share of landfilled municipal waste to below 5% of total waste generated.
Municipal waste generated and landfilled, 2014
7. Agricultural intensity
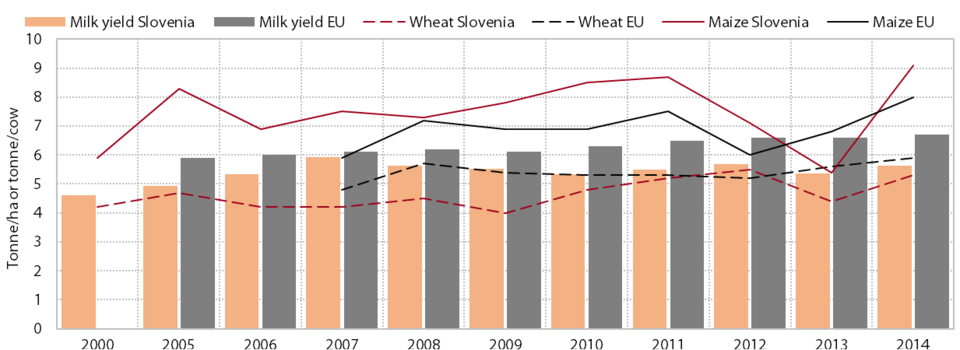
The consumption of mineral fertilisers and pesticides, which is declining in the long term, rose slightly in 2014. Agricultural producers used around 136,000 tonnes of mineral fertilisers in 2014, around a third of which were main macronutrients (NPK fertilisers, i.e. nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium). This was around 3% more than in 2013, but around 13% less or – per unit of utilised agricultural area (UAA) – around 11% less than the average for the last ten years. The total quantity of active ingredients in pesticides sold was approximately 1,000 tonnes; around two-thirds were used in agriculture, according to the preliminary estimate. Total pesticide sales were about 10% higher than in 2013, but 16% lower than the average for the last ten years. The majority of pesticides sold were fungicides for plant disease control, followed by herbicides for weed control.
Agricultural efficiency as measured by average yields of the most important crops fluctuates between the years depending on weather conditions, while agricultural efficiency as measured by the milk yield per animal is improving. Under the impact of very favourable weather conditions, the average yield per hectare increased for both main crops in 2014, by approximately one-fifth for wheat and two-thirds for maize. In both, this figure was also up on the ten-year average. As this was not too high, the increase may also indicate better exploitation of natural resources than in previous years. The relatively low average milk yield per animal is also rising in the long term, which is favourable from the perspective of the environmental burden per output. The total environmental burden per output measured by the number of animals per unit of agricultural area is relatively high but has been declining in the last few years according to surveys.
The share of agricultural holdings involved in controlled organic farming is rising and exceeds the EU average. Around 5% of agricultural holdings with around 9% of UAA were involved in controlled organic farming in 2014, which is less than planned but higher than the EU average. Only the area of agricultural holdings with a certificate for organic farming was up in 2014, while the area in conversion to organic farming declined. The largest share is accounted for by permanent grassland intended for animal production, but the fastest growth is recorded for other types of land, where production is driven by high demand. Under the impact of favourable weather conditions, total organic crop production rose notably in 2014; the production of animals was also up.
Average yields of main crops and milk production
8. Intensity of tree felling
Tree-felling is increasing in the long term, but in 2014 it was particularly pronounced as a result of emergency removals in the aftermath of the severe ice storm that year. Around 6.4 million m3 of wood was cut in 2014, which is 62% more than in 2013 and almost twice the average annual removal since 2000. For the first time since measurements began, tree felling reached (and slightly exceeded) the potential for felling determined in the forestry management plans, in contrast to previous years when only two-thirds of the felling permitted was carried out. As a consequence of severe ice damage, most of the removal (two-thirds) was for sanitation purposes, whereas felling for tree-tending purposes, which normally accounts for the largest share, declined. Amid a renewed slight increase in the annual wood increment, the tree-felling intensity rose significantly in 2014, by 28 percentage points, to 74%. In terms of volume (but not structure), this figure is very close to that envisaged in the action plan, according to which the tree-felling intensity could be increased to 75%, and 6.5 million m3 of wood could be cut per year without jeopardising sustainable development.
The increased felling is reflected in the higher production of raw wood categories and, in turn, higher net exports; the untapped potential in the forest-wood chain remains relatively large. In 2014 around 5.3 million m3 of roundwood (i.e. unprocessed wood) was obtained, approximately 50% more than in 2013 and 85% more than the average since 2000. The consequences of the ice storm were strongly reflected in the structure of industrial wood: the volume of pulpwood, which is low-quality wood that generates low value added, rose the most, while the volume of the highest quality wood, sawlogs and veneer logs, increased the least. With around half of the year-on-year increase in unprocessed wood production being exported, total annual wood exports – which had been growing for a long period – rose by 54%. As total imports contracted by around one-fifth, net wood exports almost doubled, reaching 1.9 million m3. Within those, net exports of the highest-quality wood also expanded notably (by 60% or almost 400,000 m3), although its production increased the least (by 25% or 420,000 m3).
Tree felling and the structure of wood by category, Slovenia
9. Environmental taxes
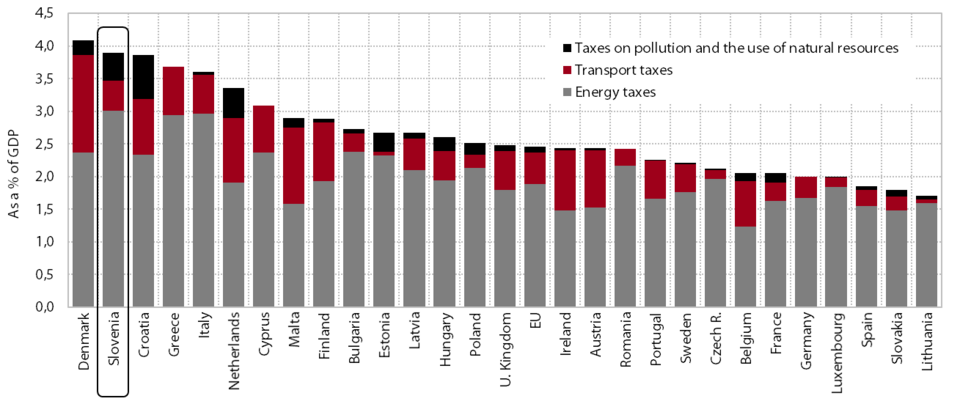
In 2014 revenue from environmental taxes as a share of GDP declined slightly after several years of almost uninterrupted growth, but was still significantly higher than before the crisis due to the high excise duties on energy. As a result of higher excise duty rates and higher or new other taxes (the introduction of the CO2 tax on motor fuels, the sale of emission allowances, the increase in annual road user charges), revenue from environmental taxes relative to GDP was 0.9 percentage points higher in 2014 than in 2008 and 0.7 percentage points higher than in 2005. In 2014 this figure fell slightly owing to the growth of revenue from excise duties on liquid fuels lagging behind GDP growth and a small decline in the inflows of taxes on environmental pollution (partly due to a reduction in the tax on the use of fluorinated greenhouse gases).
More than three-quarters of environmental taxes are accounted for by energy taxes, with taxes on pollution and transport gaining importance in recent years. Revenue from taxes on energy accounted for 77% of environmental taxes collected in 2014, the bulk being from excise duties on liquid fuels. Their consumption is relatively high in Slovenia, given the large volume of transit and other road transport, which is related, among other things, to its dispersed settlement pattern and poorly developed public transport infrastructure. In the past few years, a somewhat higher share of environmental tax revenues was raised from: (i) taxes on transport, which reached a 12% share in 2014, the bulk arising from annual road user charges; and (ii) taxes on pollution, which accounted for a 9% share in 2014 as a result of the more broadly based tax on CO2 emissions. The share of taxes on the use of natural resources, which is low, was stable. Most of the environmental tax burden, around two-thirds, was borne by households, which can be attributed in part to methodological simplification, according to which most of motor fuel consumption, and hence energy taxes, is ascribed to households.
Among EU Member States, only Denmark outpaces Slovenia in terms of its environmental tax burden relative to GDP. In 2014 revenue from environmental taxes as a share of GDP was 1.4 percentage points higher in Slovenia than the EU average. The high share is mainly due to the extensive use of motor fuels in road transport, with the tax rate on energy also being relatively high. Totalling EUR 236.4 per tonne of oil equivalent of final energy consumption, the implicit tax rate on energy in 2014 was only slightly above the weighted EU average and 17% above the unweighted EU average.
Revenue from environmental taxes, Slovenia and the EU, 2014
10. Regional variation in GDP per capita
Economic activity measured by the real GDP growth rate was positive in 2014 in all regions except the Zasavska region. The highest economic growth rates were again recorded by the Gorenjska and the Primorsko-notranjska regions. In the Zasavska region, economic growth was still negative, but to a lesser extent than in 2013. At around 58% of the national average, Zasavska also recorded the lowest GDP per capita. The Osrednjeslovenska region was again the only region that surpassed the national average, by around 42%.
Having widened during the crisis, Slovenia’s gap with the EU average in GDP per capita narrowed in 2014 in both cohesion regions. Zahodna Slovenija was close to the EU average, while Vzhodna Slovenija lagged more than 30% behind (in 2008, Zahodna was at 108% and Vzhodna at 73% of the EU average in this comparison). After 2008 the gap with the EU average widened across all regions, notably those of Zahodna Slovenija, particularly the Obalno-kraška region. In 2014 the latter increased its gap relative to 2008 by 14 index points. Among the regions of Vzhodna Slovenija, Zasavska widened the gap the most, by 15 index points. In all regions these developments reversed in 2014, as none of the regions increased their gaps. One of the regions, Osrednjeslovenska, exceeded the EU average throughout the period under observation. In 2014 it surpassed it by 17%, which was 12 index points less than in 2008.
The crisis had a seemingly favourable impact on interregional disparities, which have narrowed since peaking in 2010. According to our calculations, the relative dispersion of GDP per capita has been decreasing since 2010, but not as a result of a balanced regional development policy. The decline is attributable instead to a larger fall in economic activity in those regions that generate the largest share of Slovenia’s GDP and also have the highest GDP per capita. The relative dispersion in Slovenia is one of the lowest in the EU. The ratio between the two regions with extreme values of per capita GDP is also relatively low compared with other countries in the EU, where the differences may even be 10-fold (e.g. the United Kingdom), but this is understandable given Slovenia’s small size. In 2014 the trends from previous years continued in Slovenia and the ratio increased only slightly, from 1:2.4 to 1:2.5.
11. Regional variation in the registered unemployment rate
In 2015 the registered unemployment rate continued to fall in all regions, except Pomurska. The largest decline was recorded by the Zasavska region; however, this was mainly a statistical effect because, under the new NUTS 3 regulation, Zasavska now also includes Litija, a municipality with a below-average registered unemployment rate, while the other three municipalities of this region still have above-average rates. The registered unemployment rate in the Zasavska region declined by 2.5 percentage points (but by only 1 percentage point excluding these changes). Not including the statistical effect, the registered unemployment rate dropped the most in the Koroška region, by 1.5 percentage points. Above-average rates were recorded by the same regions as in the previous year, all of which, with the exception of Primorsko-notranjska, are located in the cohesion region of Vzhodna Slovenija. The highest rate was posted by the Pomurska region, where it rose by 0.5 percentage points to 18.9% and surpassed the national average by more than half. The lowest rate, almost a third below the national average, was once again recorded in the Gorenjska region (at 8.6%).
Interregional disparities in the registered unemployment rate measured by absolute dispersion have been stable in the last four years. In the early years of the crisis, interregional disparities had been rising, reaching their peak in 2010, when the dispersion rate was 2.4%. After 2010, however, they declined, owing to a faster increase in unemployment in those regions of Zahodna Slovenija with below-average rates; in the last four years, they remained relatively stable, with small year-on-year fluctuations. In 2015 they amounted to 1.8% of GDP, which is 0.1 percentage points more than a year earlier. On the other hand, the ratio between the two regions with extreme values increased from 1:1.9 to 1:2.2, reflecting the higher rate of registered unemployment in the Pomurska and the lower rate in the Gorenjska region.
In all regions, young people were the group of unemployed that was disproportionately affected by the contraction of the labour market during the crisis. After 2013, when the total registered unemployment rate had already started to fall across the regions, the registered unemployment rate for young people aged 15–29 had still been rapidly rising, especially in the Zasavska, Primorsko-notranjska and Osrednjeslovenska regions, and reached its peak in 2014. In 2015 it otherwise declined in all regions, the most in Zasavska (by 5.5 percentage points), but was still at least 1.5 times as high as the total rate. It was highest in the Pomurska region, at 29.8%, which is 2.2 times as much as in the Gorenjska region, which has the lowest rate.
Registered unemployment rates by region, 2015